| Subsampling | Algorithms | Overall | HGSOC | CCOC | ENOC | MUOC | LGSOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| none | rf | 0.922 | 0.948 | 0.983 | 0.953 | 0.975 | 0.984 |
| svm | 0.92 | 0.947 | 0.982 | 0.955 | 0.975 | 0.982 | |
| xgb | 0.807 | 0.809 | 0.936 | 0.933 | 0.955 | 0.982 | |
| mr | 0.807 | 0.807 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.955 | 0.982 | |
| down | rf | 0.804 | 0.853 | 0.975 | 0.903 | 0.959 | 0.92 |
| svm | 0.793 | 0.833 | 0.973 | 0.884 | 0.969 | 0.928 | |
| xgb | 0.784 | 0.829 | 0.968 | 0.893 | 0.968 | 0.911 | |
| mr | 0.827 | 0.869 | 0.977 | 0.911 | 0.961 | 0.937 | |
| up | rf | 0.928 | 0.955 | 0.983 | 0.959 | 0.979 | 0.982 |
| svm | 0.92 | 0.951 | 0.974 | 0.951 | 0.979 | 0.985 | |
| xgb | 0.933 | 0.96 | 0.985 | 0.963 | 0.977 | 0.981 | |
| mr | 0.89 | 0.924 | 0.975 | 0.948 | 0.965 | 0.968 | |
| smote | rf | 0.921 | 0.955 | 0.98 | 0.953 | 0.97 | 0.984 |
| svm | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.979 | 0.954 | 0.978 | 0.981 | |
| xgb | 0.924 | 0.955 | 0.982 | 0.956 | 0.974 | 0.982 | |
| mr | 0.898 | 0.932 | 0.979 | 0.948 | 0.968 | 0.968 | |
| hybrid | rf | 0.922 | 0.953 | 0.98 | 0.952 | 0.975 | 0.983 |
| svm | 0.916 | 0.944 | 0.982 | 0.951 | 0.975 | 0.979 | |
| xgb | 0.923 | 0.957 | 0.979 | 0.954 | 0.974 | 0.982 | |
| mr | 0.895 | 0.931 | 0.979 | 0.947 | 0.967 | 0.967 |
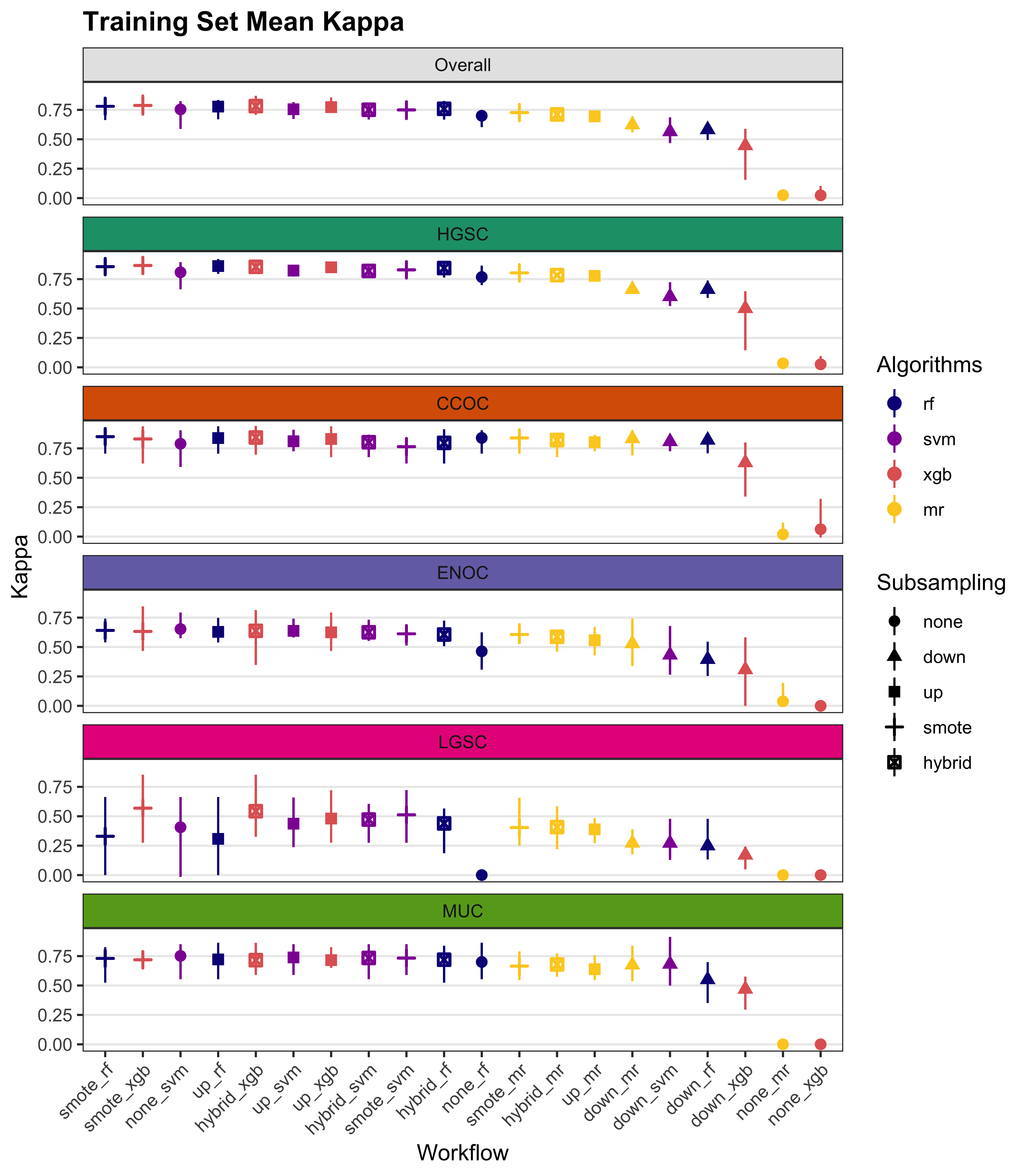
4 Results
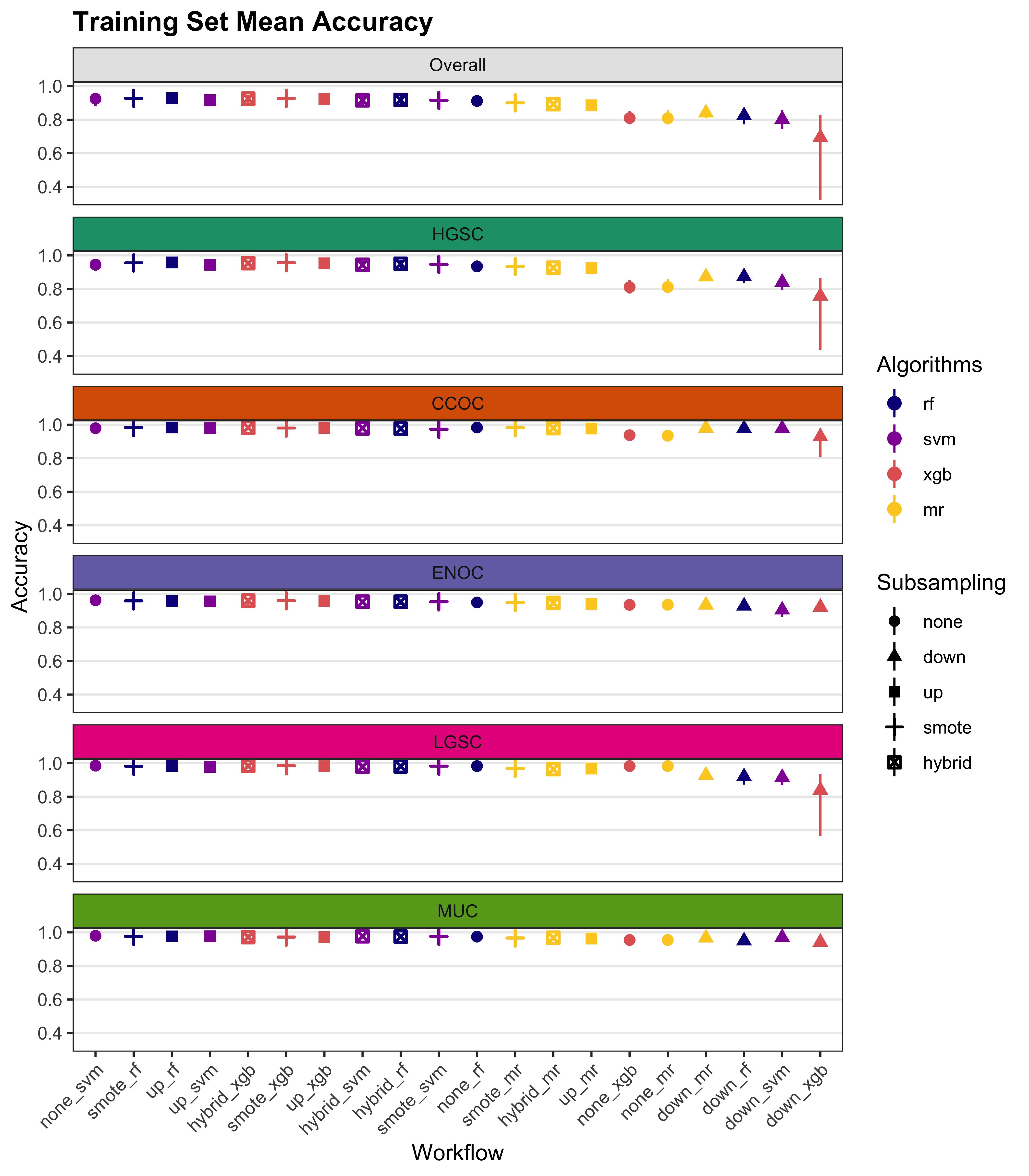
We summarize cross-validated training performance of class metrics in the training set. The accuracy, F1-score, and kappa, are the metrics of interest. Workflows are ordered by their mean estimates across the outer folds of the nested CV for each metric.
4.1 Training Set
| Subsampling | Algorithms | Overall | HGSOC | CCOC | ENOC | MUOC | LGSOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| none | rf | 0.636 | 0.994 | 0.794 | 0.498 | 0.728 | 0.167 |
| svm | 0.615 | 0.989 | 0.762 | 0.576 | 0.751 | 0 | |
| xgb | 0.2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| mr | 0.2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| down | rf | 0.742 | 0.83 | 0.827 | 0.565 | 0.657 | 0.833 |
| svm | 0.779 | 0.805 | 0.759 | 0.611 | 0.836 | 0.883 | |
| xgb | 0.753 | 0.798 | 0.82 | 0.545 | 0.837 | 0.767 | |
| mr | 0.775 | 0.846 | 0.831 | 0.62 | 0.77 | 0.808 | |
| up | rf | 0.673 | 0.988 | 0.793 | 0.635 | 0.766 | 0.183 |
| svm | 0.714 | 0.976 | 0.735 | 0.625 | 0.71 | 0.525 | |
| xgb | 0.725 | 0.981 | 0.817 | 0.679 | 0.8 | 0.35 | |
| mr | 0.787 | 0.92 | 0.845 | 0.666 | 0.786 | 0.717 | |
| smote | rf | 0.658 | 0.984 | 0.748 | 0.618 | 0.75 | 0.192 |
| svm | 0.759 | 0.966 | 0.757 | 0.681 | 0.748 | 0.642 | |
| xgb | 0.741 | 0.974 | 0.829 | 0.606 | 0.781 | 0.517 | |
| mr | 0.784 | 0.932 | 0.821 | 0.666 | 0.786 | 0.717 | |
| hybrid | rf | 0.72 | 0.972 | 0.805 | 0.638 | 0.804 | 0.383 |
| svm | 0.764 | 0.957 | 0.793 | 0.696 | 0.733 | 0.642 | |
| xgb | 0.747 | 0.971 | 0.815 | 0.604 | 0.78 | 0.567 | |
| mr | 0.784 | 0.93 | 0.809 | 0.666 | 0.75 | 0.767 |
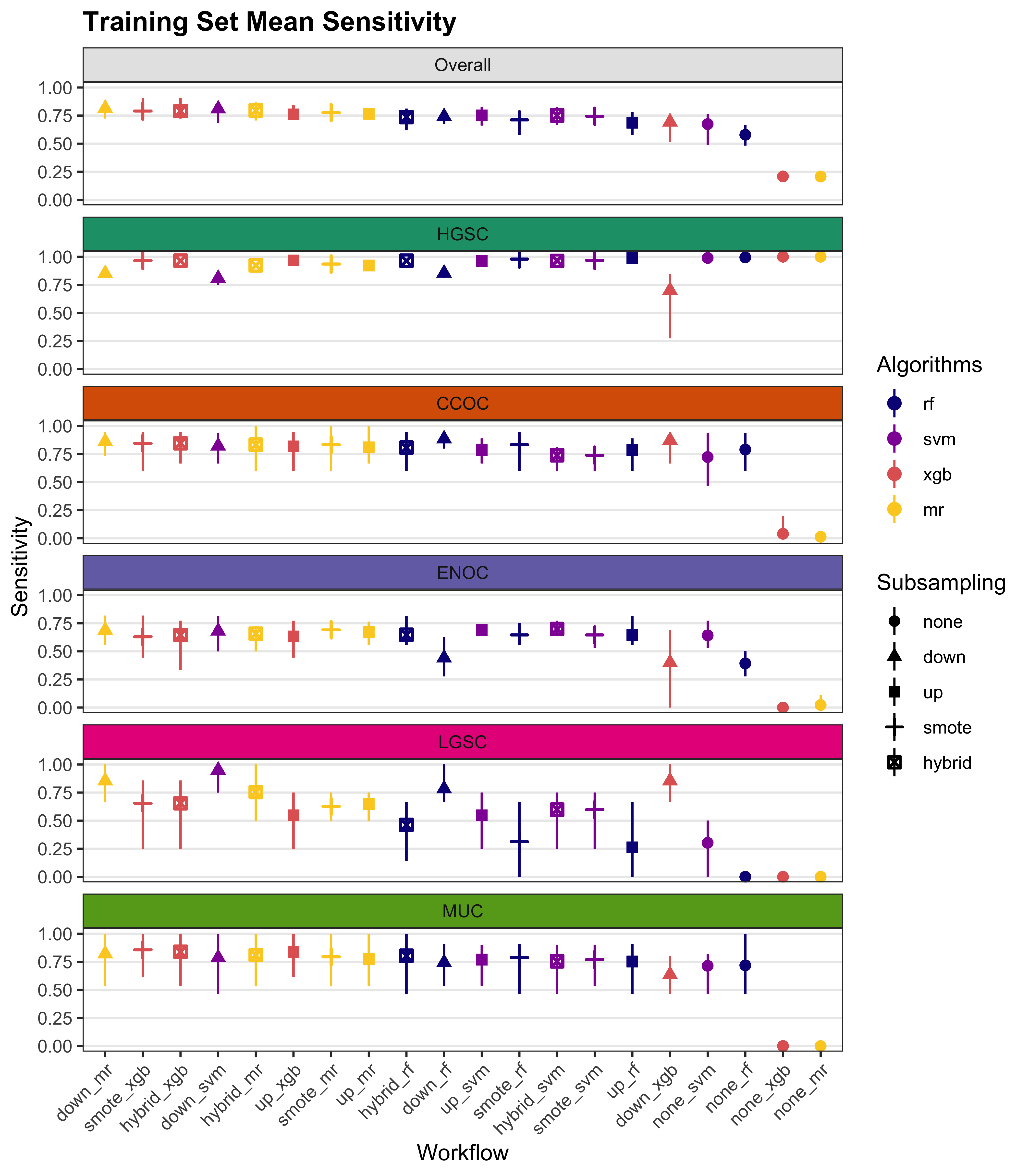
| Subsampling | Algorithms | Overall | HGSOC | CCOC | ENOC | MUOC | LGSOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| none | rf | 0.946 | 0.764 | 0.996 | 0.985 | 0.988 | 0.999 |
| svm | 0.947 | 0.775 | 0.997 | 0.98 | 0.986 | 1 | |
| xgb | 0.802 | 0.009 | 1 | 0.998 | 1 | 1 | |
| mr | 0.8 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| down | rf | 0.952 | 0.955 | 0.984 | 0.928 | 0.973 | 0.921 |
| svm | 0.949 | 0.952 | 0.987 | 0.902 | 0.976 | 0.928 | |
| xgb | 0.949 | 0.962 | 0.978 | 0.917 | 0.975 | 0.913 | |
| mr | 0.958 | 0.963 | 0.986 | 0.93 | 0.971 | 0.939 | |
| up | rf | 0.957 | 0.822 | 0.996 | 0.98 | 0.989 | 0.997 |
| svm | 0.958 | 0.844 | 0.99 | 0.973 | 0.992 | 0.993 | |
| xgb | 0.966 | 0.875 | 0.996 | 0.981 | 0.986 | 0.993 | |
| mr | 0.967 | 0.937 | 0.984 | 0.967 | 0.974 | 0.973 | |
| smote | rf | 0.958 | 0.839 | 0.996 | 0.975 | 0.981 | 0.998 |
| svm | 0.964 | 0.88 | 0.993 | 0.971 | 0.989 | 0.987 | |
| xgb | 0.965 | 0.878 | 0.992 | 0.98 | 0.983 | 0.991 | |
| mr | 0.968 | 0.934 | 0.99 | 0.967 | 0.977 | 0.973 | |
| hybrid | rf | 0.964 | 0.874 | 0.992 | 0.974 | 0.984 | 0.994 |
| svm | 0.965 | 0.89 | 0.994 | 0.968 | 0.987 | 0.985 | |
| xgb | 0.968 | 0.9 | 0.99 | 0.977 | 0.983 | 0.99 | |
| mr | 0.967 | 0.934 | 0.99 | 0.965 | 0.978 | 0.97 |
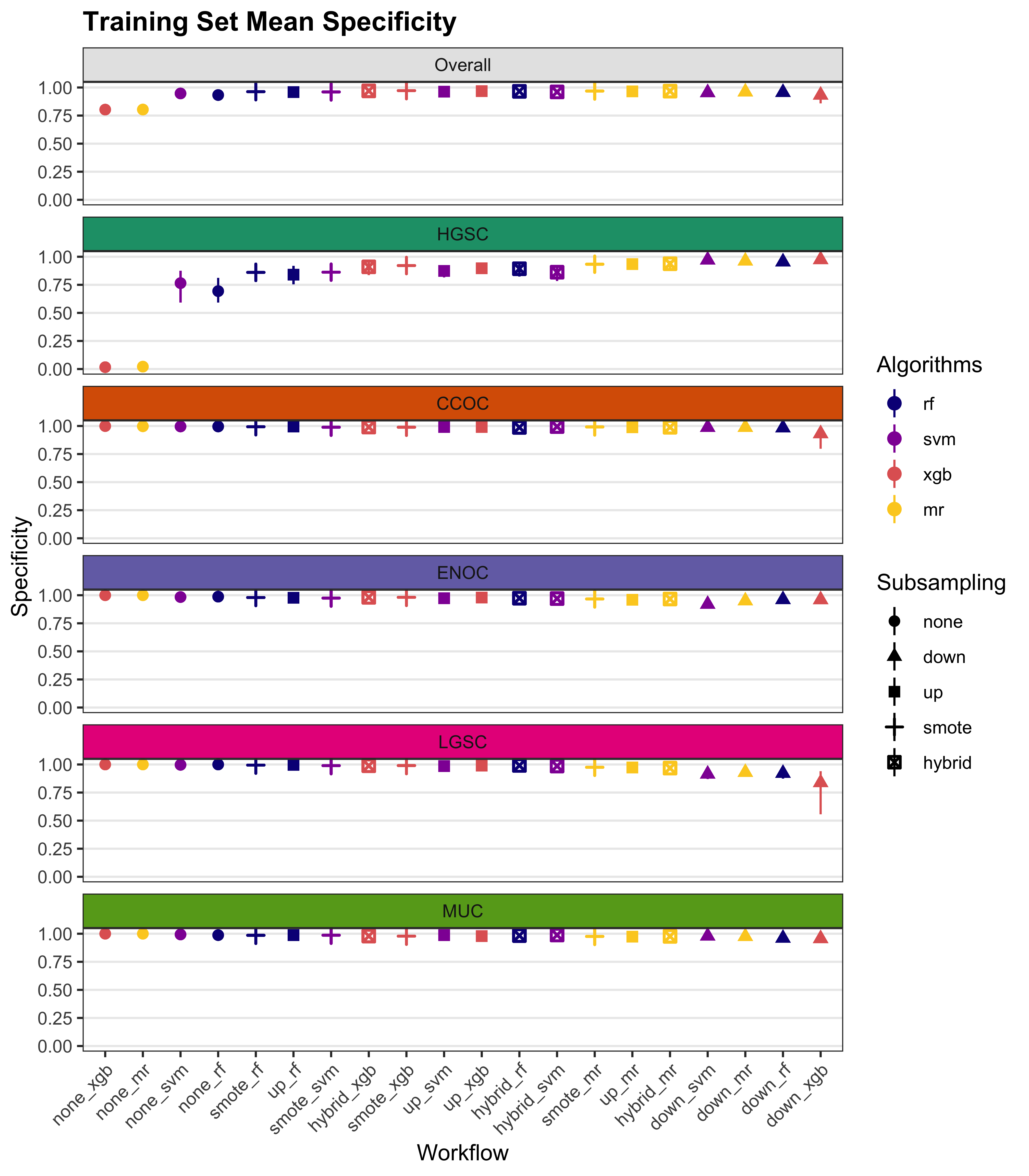
| Subsampling | Algorithms | Overall | HGSOC | CCOC | ENOC | MUOC | LGSOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| none | rf | 0.733 | 0.968 | 0.848 | 0.568 | 0.723 | 0.4 |
| svm | 0.782 | 0.968 | 0.834 | 0.607 | 0.719 | NaN | |
| xgb | 0.712 | 0.894 | NaN | 0 | NaN | NaN | |
| mr | 0.893 | 0.893 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | |
| down | rf | 0.594 | 0.901 | 0.799 | 0.419 | 0.589 | 0.262 |
| svm | 0.617 | 0.886 | 0.778 | 0.412 | 0.713 | 0.295 | |
| xgb | 0.597 | 0.883 | 0.768 | 0.399 | 0.706 | 0.227 | |
| mr | 0.627 | 0.912 | 0.817 | 0.468 | 0.638 | 0.299 | |
| up | rf | 0.755 | 0.972 | 0.849 | 0.652 | 0.757 | 0.362 |
| svm | 0.725 | 0.97 | 0.778 | 0.605 | 0.75 | 0.521 | |
| xgb | 0.729 | 0.975 | 0.862 | 0.685 | 0.753 | 0.368 | |
| mr | 0.694 | 0.951 | 0.808 | 0.616 | 0.67 | 0.428 | |
| smote | rf | 0.68 | 0.972 | 0.82 | 0.616 | 0.688 | 0.304 |
| svm | 0.739 | 0.969 | 0.811 | 0.638 | 0.752 | 0.524 | |
| xgb | 0.73 | 0.972 | 0.848 | 0.632 | 0.726 | 0.474 | |
| mr | 0.703 | 0.957 | 0.827 | 0.615 | 0.688 | 0.43 | |
| hybrid | rf | 0.724 | 0.971 | 0.829 | 0.631 | 0.741 | 0.45 |
| svm | 0.733 | 0.965 | 0.838 | 0.635 | 0.72 | 0.507 | |
| xgb | 0.729 | 0.973 | 0.823 | 0.615 | 0.729 | 0.503 | |
| mr | 0.699 | 0.956 | 0.821 | 0.606 | 0.675 | 0.437 |
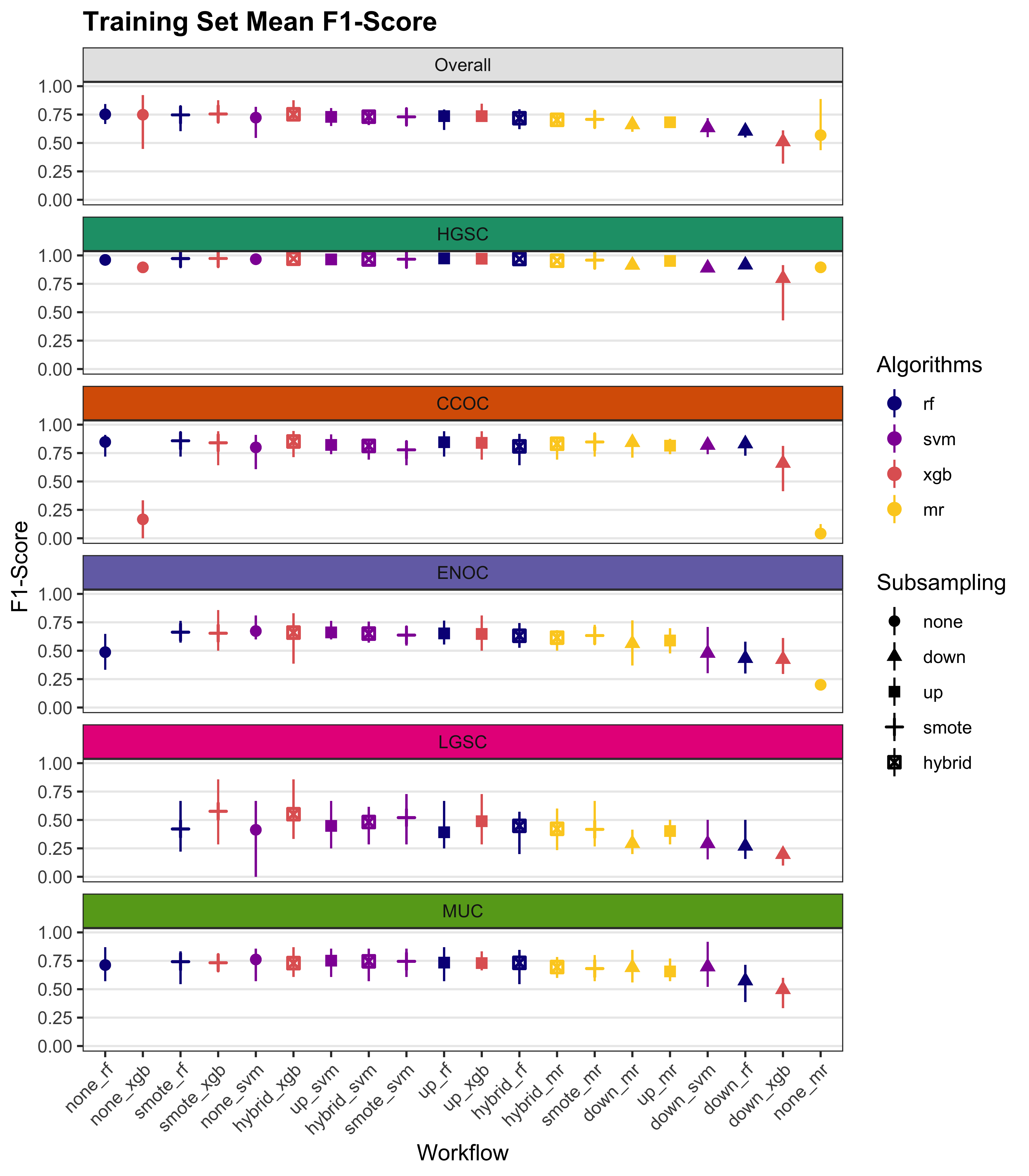
| Subsampling | Algorithms | Overall | HGSOC | CCOC | ENOC | MUOC | LGSOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| none | rf | 0.791 | 0.879 | 0.895 | 0.741 | 0.858 | 0.583 |
| svm | 0.781 | 0.882 | 0.879 | 0.778 | 0.868 | 0.5 | |
| xgb | 0.501 | 0.505 | 0.5 | 0.499 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| mr | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| down | rf | 0.847 | 0.892 | 0.905 | 0.746 | 0.815 | 0.877 |
| svm | 0.864 | 0.879 | 0.873 | 0.757 | 0.906 | 0.906 | |
| xgb | 0.851 | 0.88 | 0.899 | 0.731 | 0.906 | 0.84 | |
| mr | 0.867 | 0.905 | 0.909 | 0.775 | 0.87 | 0.874 | |
| up | rf | 0.815 | 0.905 | 0.894 | 0.808 | 0.878 | 0.59 |
| svm | 0.836 | 0.91 | 0.862 | 0.799 | 0.851 | 0.759 | |
| xgb | 0.846 | 0.928 | 0.906 | 0.83 | 0.893 | 0.671 | |
| mr | 0.877 | 0.929 | 0.914 | 0.816 | 0.88 | 0.845 | |
| smote | rf | 0.808 | 0.911 | 0.872 | 0.797 | 0.865 | 0.595 |
| svm | 0.862 | 0.923 | 0.875 | 0.826 | 0.869 | 0.814 | |
| xgb | 0.853 | 0.926 | 0.911 | 0.793 | 0.882 | 0.754 | |
| mr | 0.876 | 0.933 | 0.905 | 0.816 | 0.882 | 0.845 | |
| hybrid | rf | 0.842 | 0.923 | 0.898 | 0.806 | 0.894 | 0.689 |
| svm | 0.864 | 0.923 | 0.893 | 0.832 | 0.86 | 0.814 | |
| xgb | 0.858 | 0.936 | 0.902 | 0.79 | 0.882 | 0.778 | |
| mr | 0.876 | 0.932 | 0.899 | 0.815 | 0.864 | 0.868 |
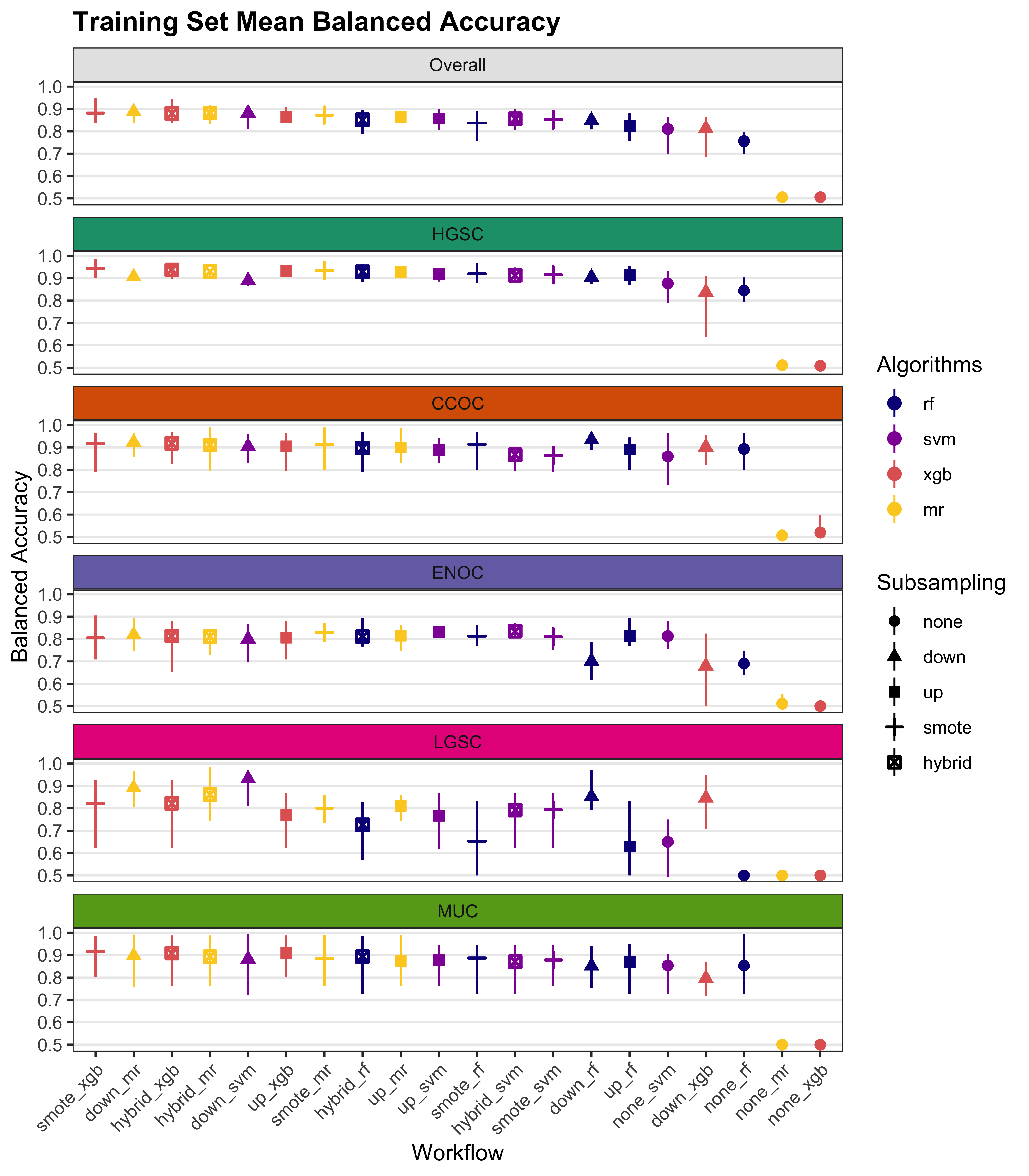
| Subsampling | Algorithms | Overall | HGSOC | CCOC | ENOC | MUOC | LGSOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| none | rf | 0.744 | 0.822 | 0.84 | 0.545 | 0.711 | 0.237 |
| svm | 0.741 | 0.818 | 0.825 | 0.583 | 0.706 | 0 | |
| xgb | 0.007 | 0.016 | 0 | -0.003 | 0 | 0 | |
| mr | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| down | rf | 0.55 | 0.621 | 0.785 | 0.37 | 0.568 | 0.24 |
| svm | 0.539 | 0.584 | 0.764 | 0.359 | 0.697 | 0.275 | |
| xgb | 0.526 | 0.578 | 0.752 | 0.348 | 0.69 | 0.204 | |
| mr | 0.592 | 0.654 | 0.805 | 0.424 | 0.618 | 0.279 | |
| up | rf | 0.776 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.63 | 0.746 | 0.213 |
| svm | 0.749 | 0.835 | 0.764 | 0.579 | 0.739 | 0.513 | |
| xgb | 0.795 | 0.871 | 0.854 | 0.666 | 0.741 | 0.36 | |
| mr | 0.705 | 0.775 | 0.795 | 0.588 | 0.652 | 0.415 | |
| smote | rf | 0.756 | 0.853 | 0.81 | 0.591 | 0.673 | 0.299 |
| svm | 0.761 | 0.839 | 0.8 | 0.614 | 0.741 | 0.516 | |
| xgb | 0.773 | 0.855 | 0.839 | 0.609 | 0.712 | 0.466 | |
| mr | 0.721 | 0.797 | 0.816 | 0.588 | 0.672 | 0.417 | |
| hybrid | rf | 0.767 | 0.85 | 0.818 | 0.605 | 0.728 | 0.443 |
| svm | 0.753 | 0.825 | 0.828 | 0.609 | 0.707 | 0.497 | |
| xgb | 0.77 | 0.863 | 0.812 | 0.59 | 0.715 | 0.494 | |
| mr | 0.713 | 0.793 | 0.81 | 0.577 | 0.658 | 0.424 |
4.2 Rank Aggregation
Multi-step methods:
- sequential: sequential algorithm sequence of subsampling methods and algorithms used are:
- HGSOC vs. non-HGSOC using upsubsampling and XGBoost
- CCOC vs. non-CCOC using no subsampling and random forest
- ENOC vs. non-ENOC using no subsampling and support vector machine
- MUOC vs. LGSOC using SMOTE subsampling and random forest
- two_step: two-step algorithm sequence of subsampling methods and algorithms used are:
- HGSOC vs. non-HGSOC using upsampling and XGBoost
- CCOC vs. ENOC vs. MUOC vs. LGSOC using SMOTE subsampling and support vector machine
We conduct rank aggregation using a two-stage nested approach:
- First we rank aggregate the per-class metrics for F1-score, balanced accuracy and kappa.
- Then we take the aggregated lists from the three metrics and perform a final rank aggregation.
- The top workflows from the final rank aggregation are used for gene optimization in the confirmation set
4.2.1 Across Classes
4.2.2 Across Metrics
| Rank | F1 | Balanced Accuracy | Kappa |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | sequential | sequential | sequential |
| 2 | two_step | two_step | two_step |
| 3 | up_xgb | up_mr | up_xgb |
| 4 | up_rf | smote_mr | up_rf |
| 5 | smote_svm | up_xgb | smote_svm |
| 6 | hybrid_svm | smote_xgb | hybrid_rf |
| 7 | smote_xgb | hybrid_mr | smote_xgb |
| 8 | hybrid_rf | hybrid_xgb | hybrid_svm |
| 9 | up_svm | down_xgb | up_svm |
| 10 | hybrid_xgb | smote_svm | hybrid_xgb |
| 11 | none_rf | hybrid_rf | smote_rf |
| 12 | smote_mr | down_mr | smote_mr |
| 13 | smote_rf | hybrid_svm | none_svm |
| 14 | hybrid_mr | up_rf | none_rf |
| 15 | up_mr | smote_rf | hybrid_mr |
| 16 | down_mr | down_rf | up_mr |
| 17 | down_rf | none_svm | down_mr |
| 18 | down_svm | down_svm | down_rf |
| 19 | down_xgb | none_rf | down_svm |
| 20 | NA | up_svm | down_xgb |
| 21 | NA | none_mr | none_mr |
| 22 | NA | none_xgb | none_xgb |
| Rank | Workflow |
|---|---|
| 1 | sequential |
| 2 | two_step |
| 3 | up_xgb |
| 4 | up_rf |
| 5 | smote_svm |
4.2.3 Top Workflows
We look at the per-class evaluation metrics of the top 5 workflows.
| Metric | Workflow | HGSOC | CCOC | ENOC | MUOC | LGSOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | sequential | 0.963 (0.956, 0.968) | 0.917 (0.896, 0.958) | 0.856 (0.774, 0.909) | 0.951 (0.882, 1) | 0.951 (0.882, 1) |
| 2-STEP | 0.963 (0.956, 0.968) | 0.934 (0.896, 0.958) | 0.839 (0.729, 0.896) | 0.892 (0.812, 0.96) | 0.971 (0.938, 1) | |
| Up-XGB | 0.96 (0.944, 0.976) | 0.985 (0.968, 0.996) | 0.963 (0.956, 0.976) | 0.977 (0.968, 0.988) | 0.981 (0.976, 0.988) | |
| Up-RF | 0.955 (0.92, 0.976) | 0.983 (0.972, 0.992) | 0.959 (0.948, 0.972) | 0.979 (0.964, 0.988) | 0.982 (0.968, 0.988) | |
| SMOTE-SVM | 0.95 (0.936, 0.968) | 0.979 (0.968, 0.988) | 0.954 (0.94, 0.964) | 0.978 (0.96, 0.984) | 0.981 (0.972, 0.984) | |
| Sensitivity | sequential | 0.978 (0.966, 0.99) | 0.814 (0.75, 0.882) | 0.865 (0.812, 0.941) | 0.965 (0.909, 1) | 0.92 (0.6, 1) |
| 2-STEP | 0.978 (0.966, 0.99) | 0.866 (0.824, 0.933) | 0.735 (0.556, 0.824) | 0.842 (0.75, 0.923) | 0.767 (0, 1) | |
| Up-XGB | 0.981 (0.976, 0.986) | 0.817 (0.571, 0.941) | 0.679 (0.444, 0.818) | 0.8 (0.538, 1) | 0.35 (0.25, 0.667) | |
| Up-RF | 0.988 (0.979, 0.995) | 0.793 (0.571, 0.882) | 0.635 (0.444, 0.812) | 0.766 (0.462, 0.909) | 0.183 (0, 0.333) | |
| SMOTE-SVM | 0.966 (0.955, 0.977) | 0.757 (0.571, 0.85) | 0.681 (0.5, 0.864) | 0.748 (0.538, 0.909) | 0.642 (0.5, 0.75) | |
| Specificity | sequential | 0.897 (0.875, 0.918) | 0.969 (0.938, 1) | 0.847 (0.733, 0.875) | 0.92 (0.6, 1) | 0.965 (0.909, 1) |
| 2-STEP | 0.897 (0.875, 0.918) | 0.969 (0.935, 1) | 0.893 (0.833, 0.935) | 0.908 (0.833, 0.973) | 0.977 (0.953, 1) | |
| Up-XGB | 0.875 (0.826, 0.919) | 0.996 (0.992, 1) | 0.981 (0.97, 0.991) | 0.986 (0.979, 0.992) | 0.993 (0.984, 1) | |
| Up-RF | 0.822 (0.738, 0.892) | 0.996 (0.992, 1) | 0.98 (0.966, 0.987) | 0.989 (0.983, 0.996) | 0.997 (0.988, 1) | |
| SMOTE-SVM | 0.88 (0.804, 0.919) | 0.993 (0.987, 1) | 0.971 (0.962, 0.975) | 0.989 (0.983, 0.996) | 0.987 (0.976, 0.996) | |
| F1-Score | sequential | 0.977 (0.973, 0.98) | 0.868 (0.828, 0.933) | 0.86 (0.788, 0.914) | 0.966 (0.923, 1) | 0.91 (0.75, 1) |
| 2-STEP | 0.977 (0.973, 0.98) | 0.899 (0.848, 0.933) | 0.755 (0.606, 0.848) | 0.788 (0.667, 0.923) | 0.733 (0, 1) | |
| Up-XGB | 0.975 (0.964, 0.986) | 0.862 (0.667, 0.97) | 0.685 (0.471, 0.857) | 0.753 (0.636, 0.87) | 0.368 (0.25, 0.571) | |
| Up-RF | 0.972 (0.949, 0.986) | 0.849 (0.696, 0.938) | 0.652 (0.471, 0.788) | 0.757 (0.571, 0.87) | 0.362 (0.286, 0.4) | |
| SMOTE-SVM | 0.969 (0.96, 0.981) | 0.811 (0.667, 0.919) | 0.638 (0.5, 0.809) | 0.752 (0.583, 0.833) | 0.524 (0.364, 0.714) | |
| Balanced Accuracy | sequential | 0.938 (0.928, 0.947) | 0.892 (0.859, 0.938) | 0.856 (0.773, 0.908) | 0.943 (0.8, 1) | 0.943 (0.8, 1) |
| 2-STEP | 0.938 (0.928, 0.947) | 0.917 (0.88, 0.952) | 0.814 (0.694, 0.88) | 0.875 (0.792, 0.948) | 0.872 (0.479, 1) | |
| Up-XGB | 0.928 (0.901, 0.952) | 0.906 (0.781, 0.971) | 0.83 (0.714, 0.905) | 0.893 (0.765, 0.99) | 0.671 (0.621, 0.829) | |
| Up-RF | 0.905 (0.858, 0.941) | 0.894 (0.784, 0.941) | 0.808 (0.714, 0.898) | 0.878 (0.727, 0.95) | 0.59 (0.5, 0.665) | |
| SMOTE-SVM | 0.923 (0.885, 0.948) | 0.875 (0.781, 0.925) | 0.826 (0.735, 0.919) | 0.869 (0.761, 0.948) | 0.814 (0.746, 0.869) | |
| Kappa | sequential | 0.879 (0.862, 0.895) | 0.808 (0.754, 0.903) | 0.712 (0.547, 0.818) | 0.877 (0.679, 1) | 0.877 (0.679, 1) |
| 2-STEP | 0.879 (0.862, 0.895) | 0.85 (0.769, 0.903) | 0.635 (0.402, 0.769) | 0.716 (0.538, 0.896) | 0.718 (-0.029, 1) | |
| Up-XGB | 0.871 (0.822, 0.905) | 0.854 (0.65, 0.968) | 0.666 (0.452, 0.844) | 0.741 (0.62, 0.863) | 0.36 (0.239, 0.566) | |
| Up-RF | 0.85 (0.768, 0.903) | 0.84 (0.682, 0.933) | 0.63 (0.452, 0.773) | 0.746 (0.554, 0.863) | 0.213 (0, 0.396) | |
| SMOTE-SVM | 0.839 (0.783, 0.876) | 0.8 (0.65, 0.913) | 0.614 (0.48, 0.789) | 0.741 (0.563, 0.825) | 0.516 (0.352, 0.706) |
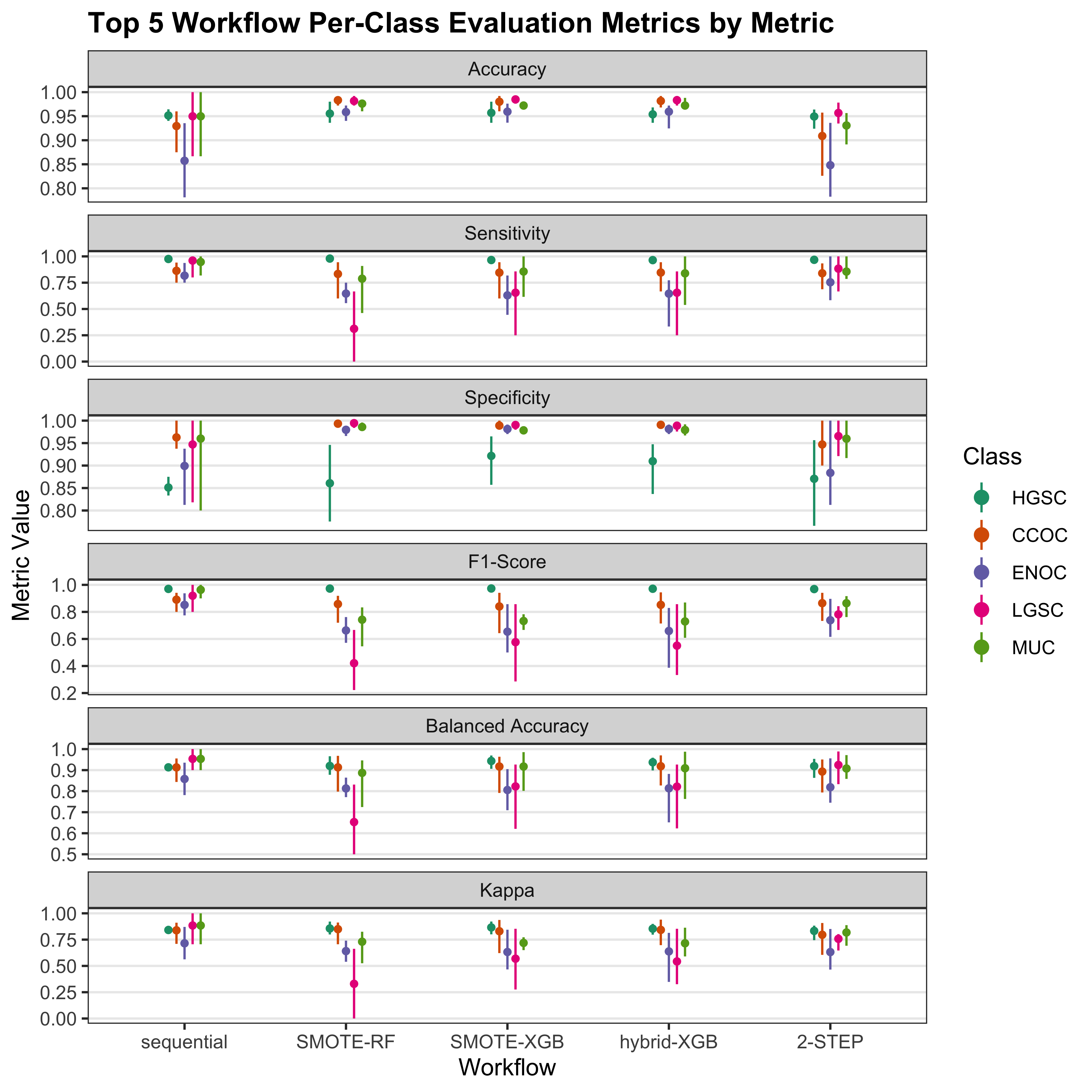
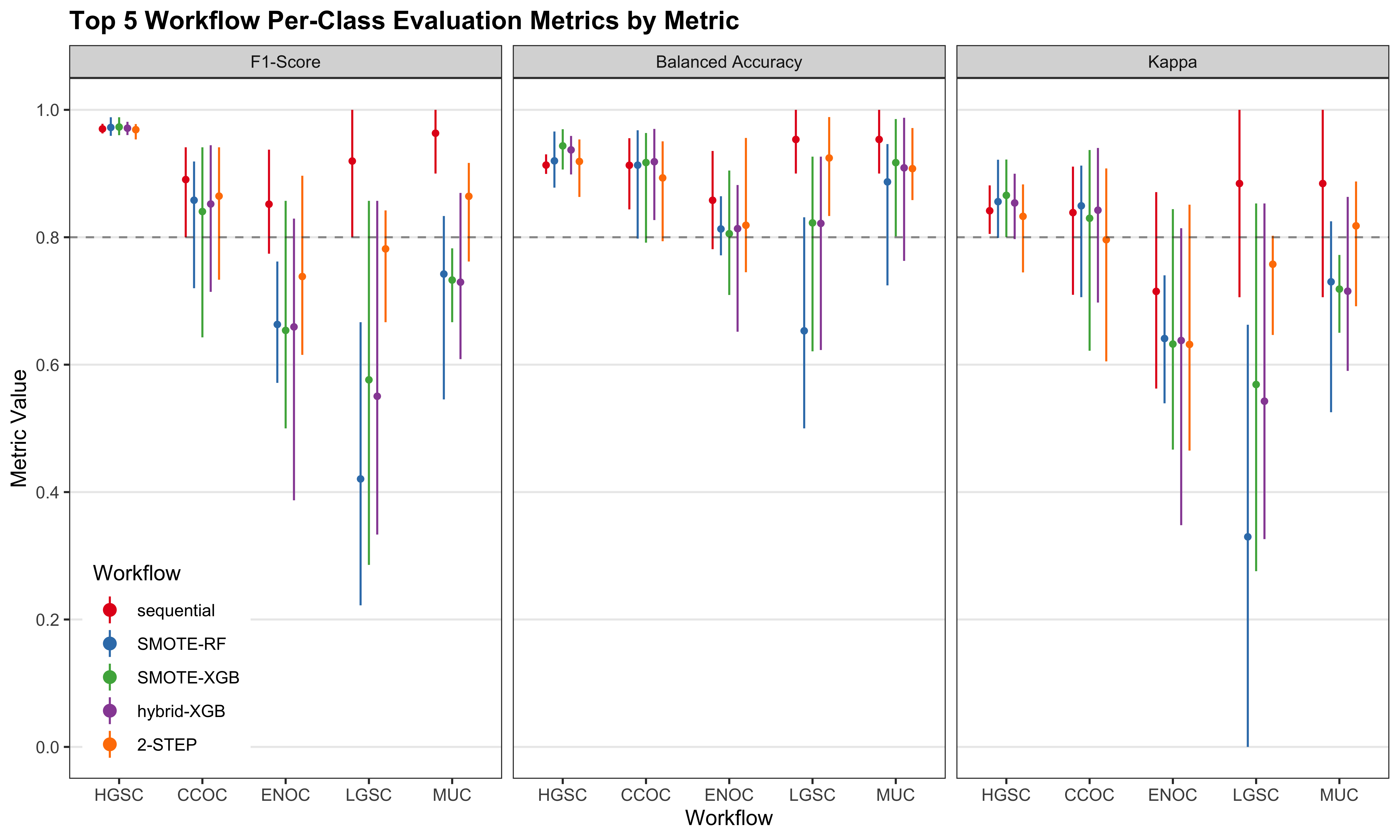
| Workflow | Rank | HGSOC | CCOC | ENOC | MUOC | LGSOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1-Score | ||||||
| sequential | 1 | 0.977 | 0.868 | 0.860 | 0.966 | 0.910 |
| 2-STEP | 2 | 0.977 | 0.899 | 0.755 | 0.788 | 0.733 |
| Up-XGB | 3 | 0.975 | 0.862 | 0.685 | 0.753 | 0.368 |
| Up-RF | 4 | 0.972 | 0.849 | 0.652 | 0.757 | 0.362 |
| SMOTE-SVM | 5 | 0.969 | 0.811 | 0.638 | 0.752 | 0.524 |
| Balanced Accuracy | ||||||
| sequential | 1 | 0.938 | 0.892 | 0.856 | 0.943 | 0.943 |
| 2-STEP | 2 | 0.938 | 0.917 | 0.814 | 0.875 | 0.872 |
| Up-XGB | 5 | 0.928 | 0.906 | 0.830 | 0.893 | 0.671 |
| SMOTE-SVM | 10 | 0.923 | 0.875 | 0.826 | 0.869 | 0.814 |
| Up-RF | 14 | 0.905 | 0.894 | 0.808 | 0.878 | 0.590 |
| Kappa | ||||||
| sequential | 1 | 0.879 | 0.808 | 0.712 | 0.877 | 0.877 |
| 2-STEP | 2 | 0.879 | 0.850 | 0.635 | 0.716 | 0.718 |
| Up-XGB | 3 | 0.871 | 0.854 | 0.666 | 0.741 | 0.360 |
| Up-RF | 4 | 0.850 | 0.840 | 0.630 | 0.746 | 0.213 |
| SMOTE-SVM | 5 | 0.839 | 0.800 | 0.614 | 0.741 | 0.516 |
Misclassified cases from a previous step of the sequence of classifiers are not included in subsequent steps of the training set CV folds. Thus, we cannot piece together the test set predictions from the sequential and two-step algorithms to obtain overall metrics.
4.3 Confirmation Set
Now we’d like to see how our best five workflows perform in the confirmation set. The class-specific F1-scores will be used. The top performing method will be selected for gene optimization.
| Method | Metric | Overall | HGSOC | CCOC | ENOC | MUOC | LGSOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequential | Accuracy | 0.830 | 0.860 | 0.977 | 0.882 | 0.969 | 0.974 |
| Sensitivity | 0.592 | 0.950 | 0.847 | 0.486 | 0.593 | 0.083 | |
| Specificity | 0.923 | 0.683 | 0.993 | 0.961 | 0.985 | 0.990 | |
| F1-Score | 0.618 | 0.900 | 0.891 | 0.578 | 0.615 | 0.105 | |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.757 | 0.817 | 0.920 | 0.723 | 0.789 | 0.537 | |
| Kappa | 0.648 | 0.670 | 0.877 | 0.512 | 0.599 | 0.093 | |
| 2-STEP | Accuracy | 0.833 | 0.860 | 0.970 | 0.889 | 0.978 | 0.969 |
| Sensitivity | 0.608 | 0.950 | 0.861 | 0.477 | 0.667 | 0.083 | |
| Specificity | 0.923 | 0.683 | 0.984 | 0.972 | 0.992 | 0.986 | |
| F1-Score | 0.633 | 0.900 | 0.867 | 0.590 | 0.720 | 0.091 | |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.766 | 0.817 | 0.923 | 0.724 | 0.829 | 0.535 | |
| Kappa | 0.655 | 0.670 | 0.850 | 0.530 | 0.709 | 0.075 | |
| Up-XGB | Accuracy | 0.844 | 0.868 | 0.970 | 0.896 | 0.980 | 0.975 |
| Sensitivity | 0.658 | 0.958 | 0.875 | 0.467 | 0.741 | 0.250 | |
| Specificity | 0.927 | 0.693 | 0.982 | 0.981 | 0.990 | 0.989 | |
| F1-Score | 0.680 | 0.905 | 0.869 | 0.599 | 0.755 | 0.273 | |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.793 | 0.825 | 0.929 | 0.724 | 0.865 | 0.619 | |
| Kappa | 0.678 | 0.688 | 0.852 | 0.544 | 0.744 | 0.260 | |
| Up-RF | Accuracy | 0.835 | 0.857 | 0.975 | 0.883 | 0.974 | 0.981 |
| Sensitivity | 0.613 | 0.972 | 0.875 | 0.383 | 0.667 | 0.167 | |
| Specificity | 0.918 | 0.633 | 0.988 | 0.983 | 0.987 | 0.997 | |
| F1-Score | 0.648 | 0.900 | 0.887 | 0.522 | 0.679 | 0.250 | |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.765 | 0.802 | 0.931 | 0.683 | 0.827 | 0.582 | |
| Kappa | 0.646 | 0.654 | 0.873 | 0.466 | 0.665 | 0.243 | |
| SMOTE-SVM | Accuracy | 0.827 | 0.866 | 0.958 | 0.888 | 0.972 | 0.970 |
| Sensitivity | 0.650 | 0.939 | 0.861 | 0.477 | 0.556 | 0.417 | |
| Specificity | 0.927 | 0.725 | 0.970 | 0.970 | 0.990 | 0.981 | |
| F1-Score | 0.656 | 0.902 | 0.821 | 0.586 | 0.625 | 0.345 | |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.788 | 0.832 | 0.916 | 0.723 | 0.773 | 0.699 | |
| Kappa | 0.651 | 0.690 | 0.797 | 0.525 | 0.611 | 0.330 |
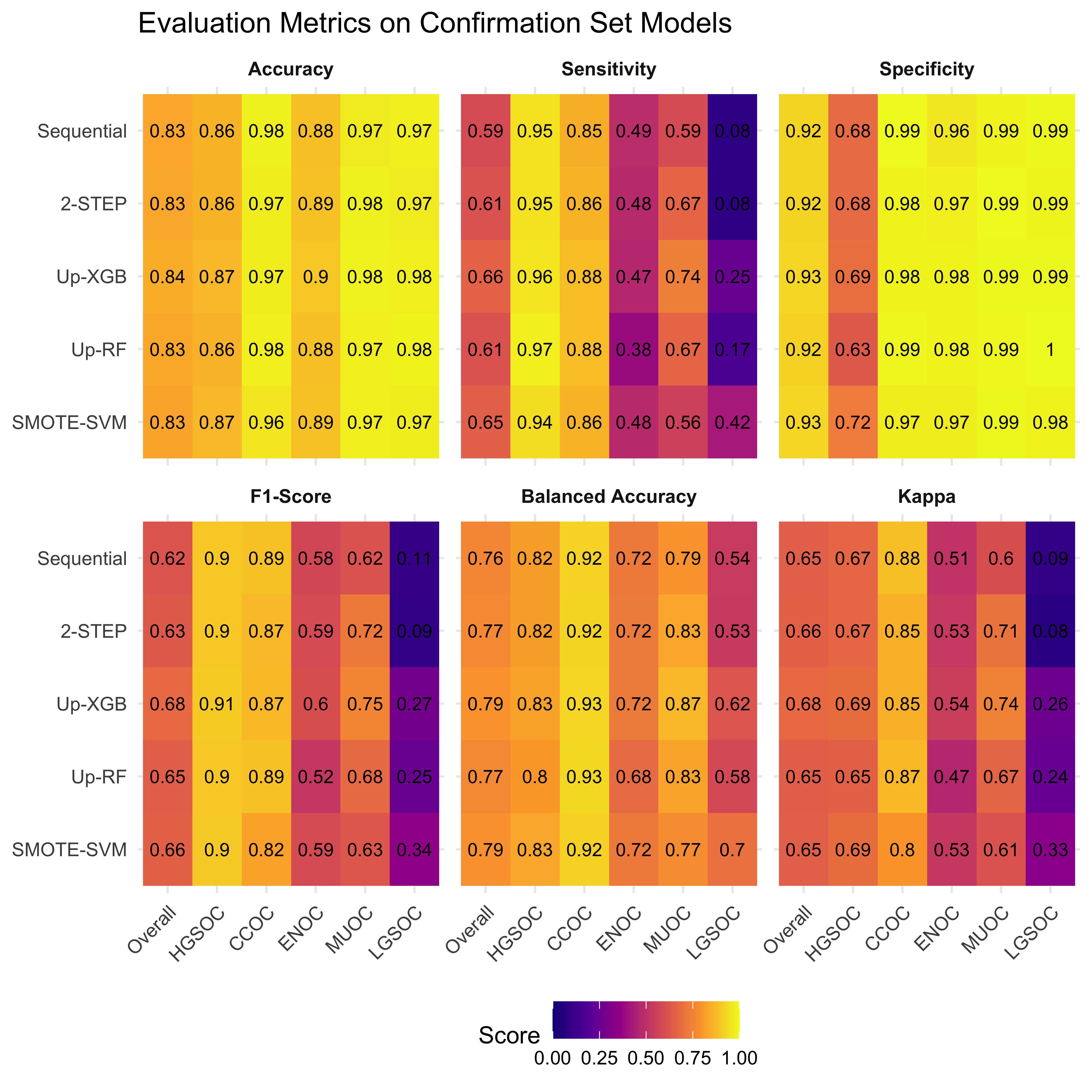
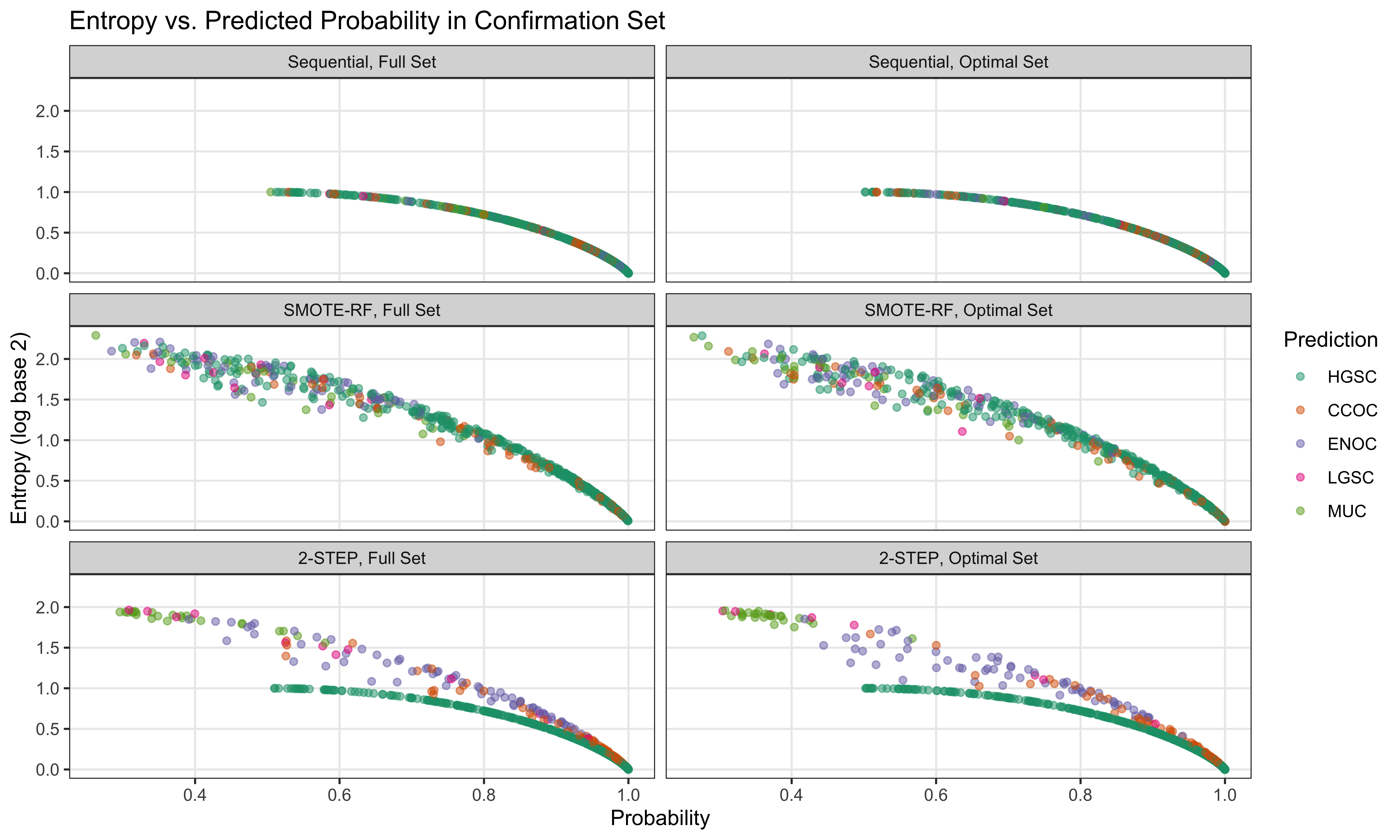
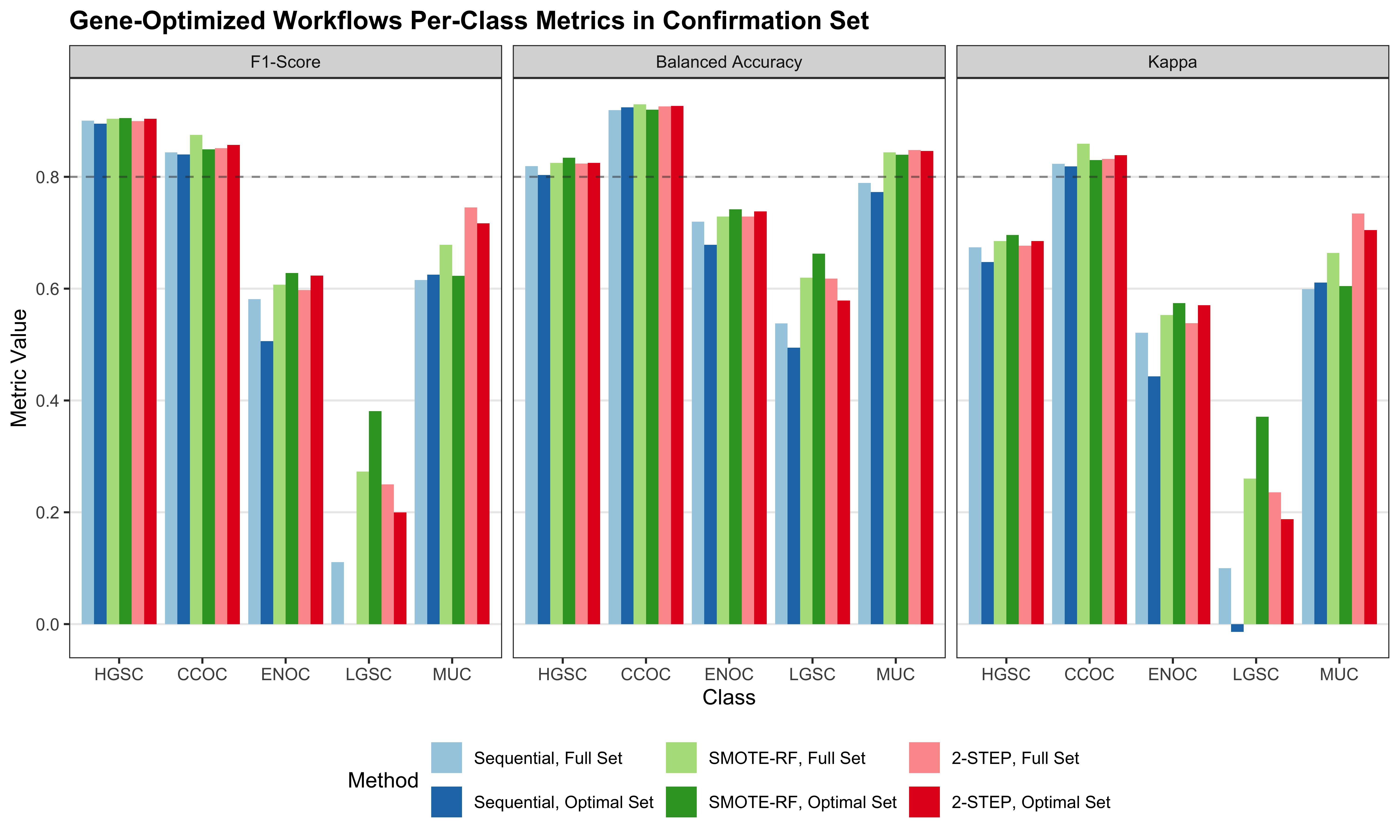
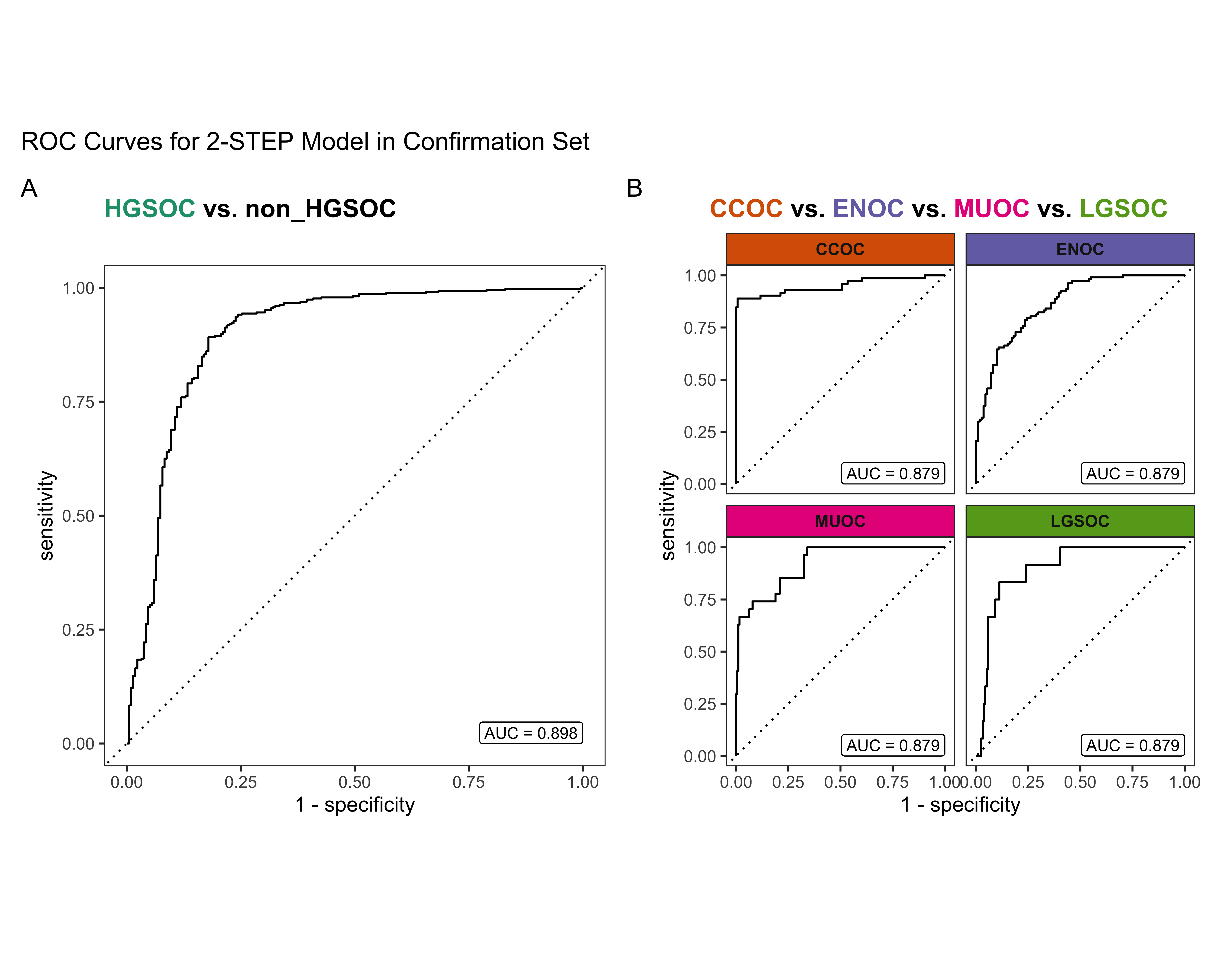
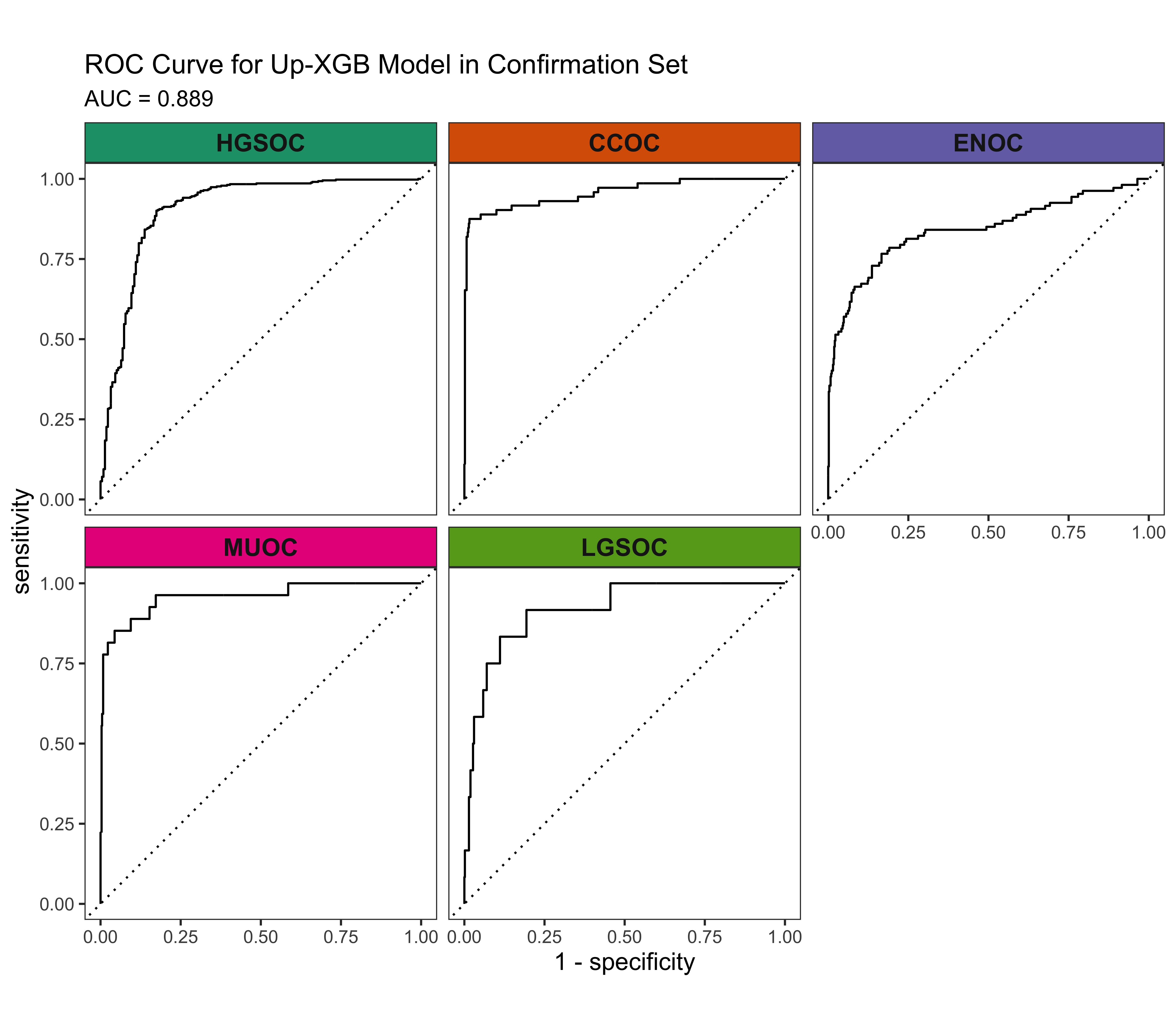
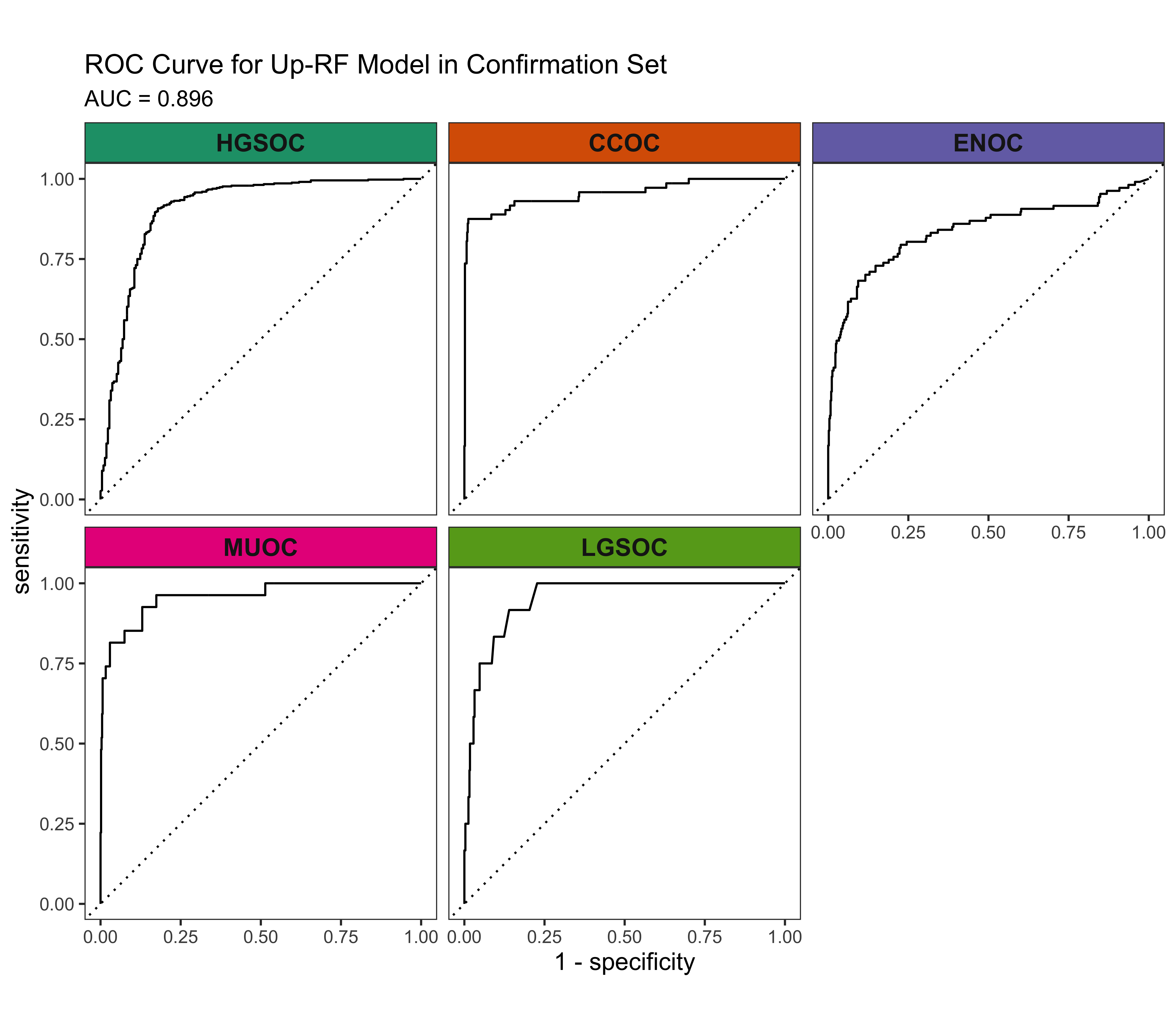
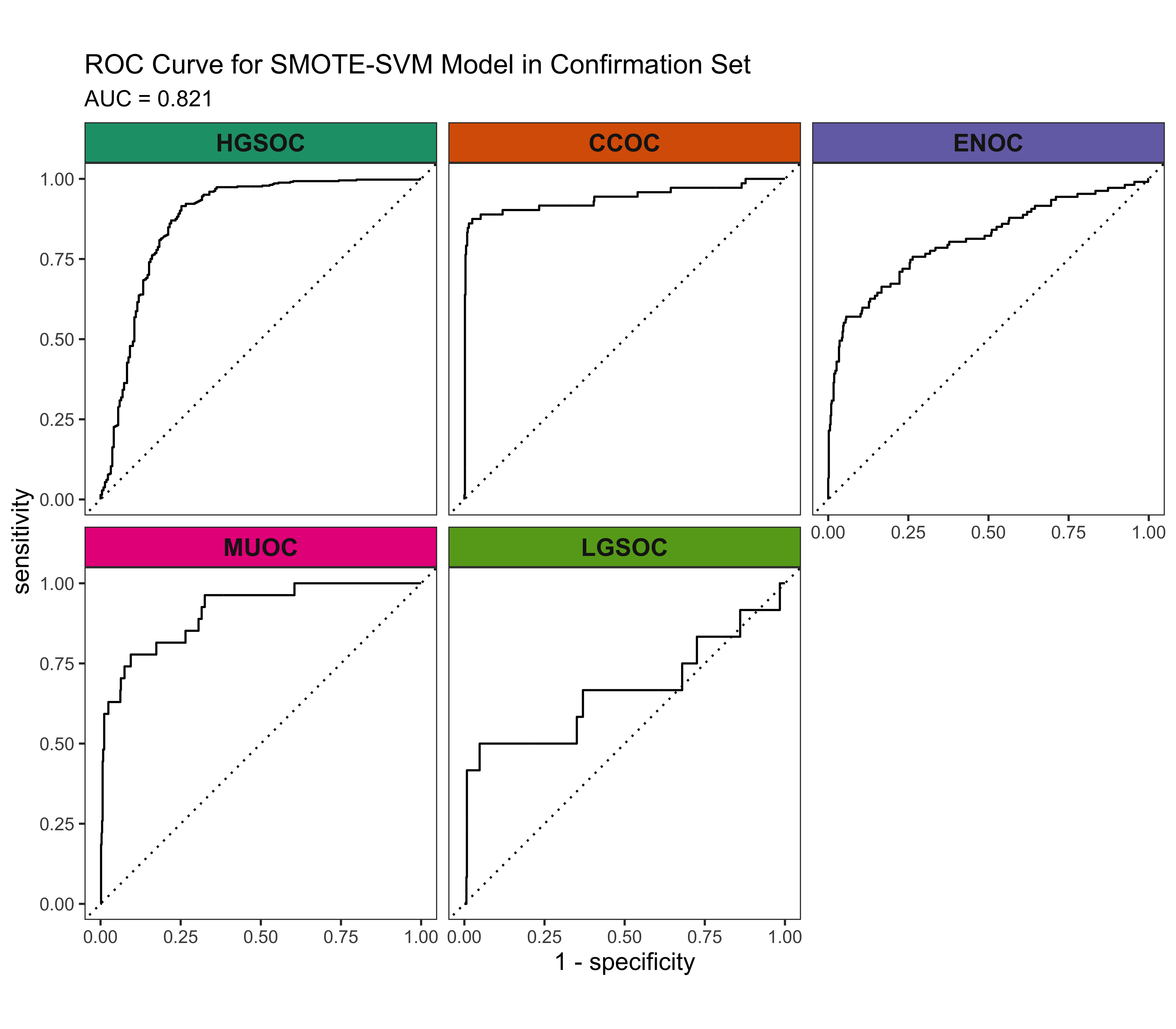
4.4 Gene Optimization
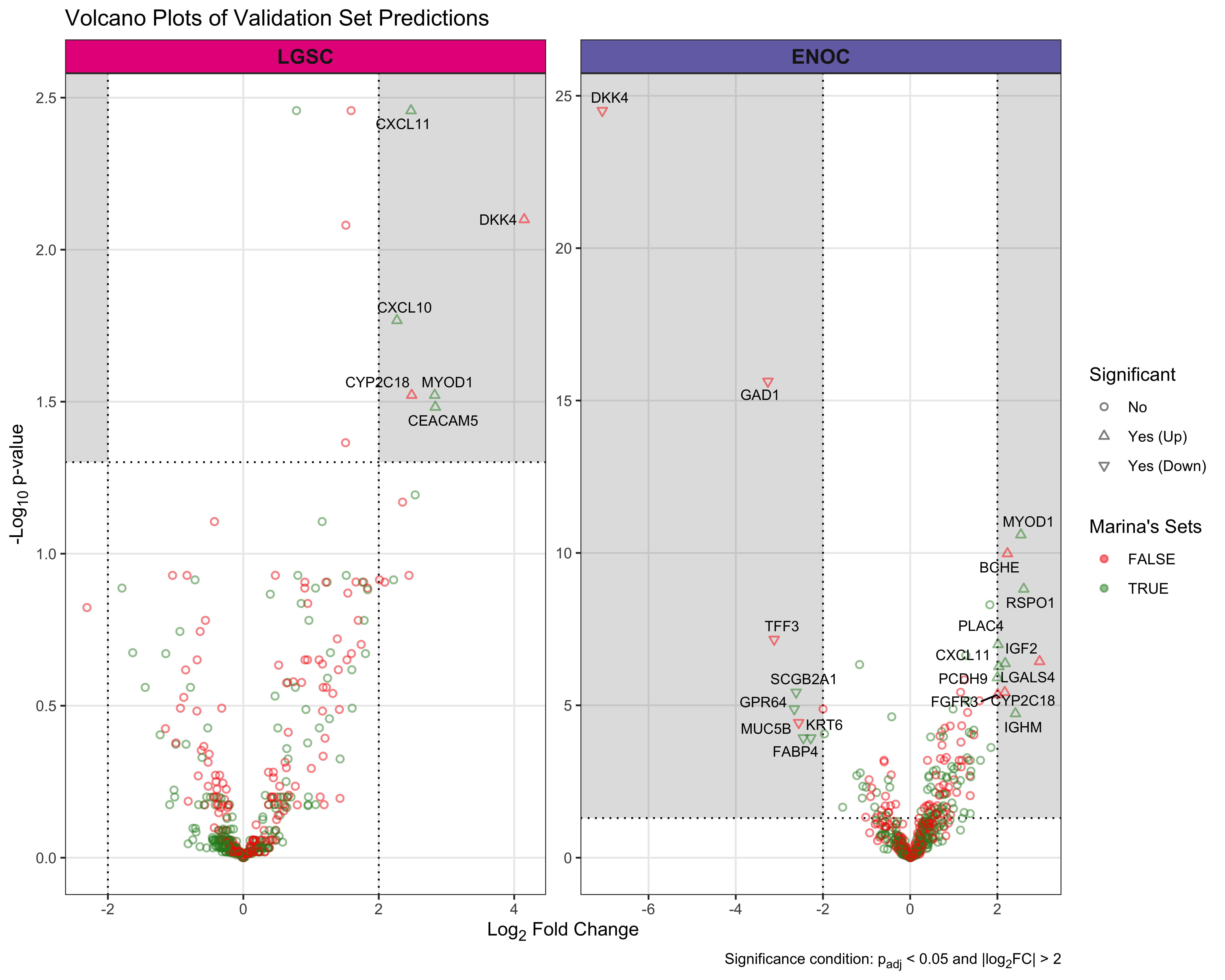
From Figure 4.9, we see that although Up-XGB has the highest overall evaluation metric scores, SMOTE-SVM is better at predicting the rarest histotype LGSOC. The other four histotypes have relatively lower predictive performance in SMOTE-SVM. With such few cases in LGSOC we decided to select the workflow that is able to discern all histotypes to a fair extent for gene optimization.
4.4.1 SMOTE-SVM
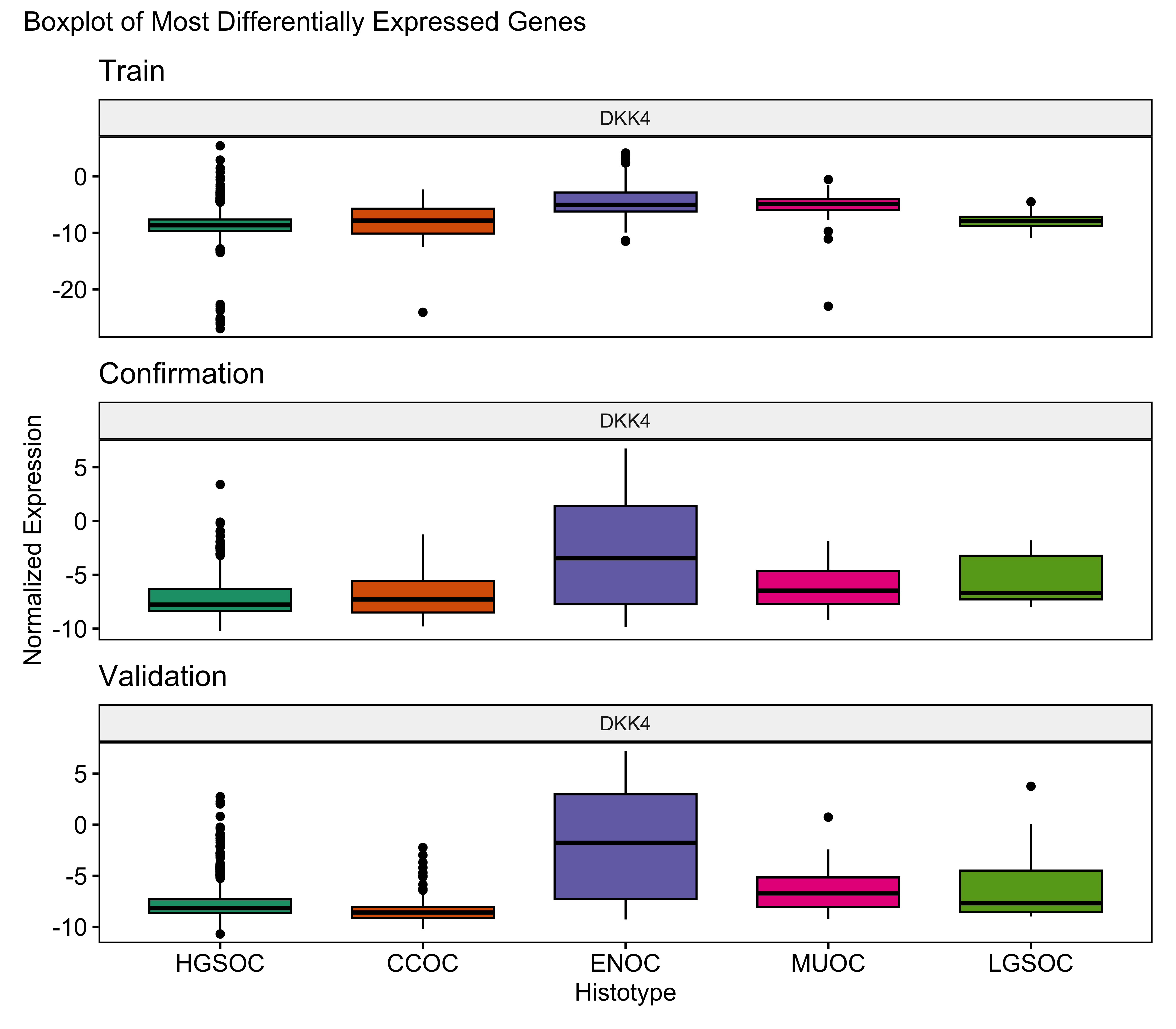
In the SMOTE-SVM classifier, the optimal number of genes is achieved at the fewest genes needed to achieve a mean F1-Score above 0.7 with 22 genes added, highlighted in red in Figure 4.18. Hence the optimal number of total genes used will be n=28+22=50.
The gene profile of the optimal set of genes used is displayed in Table 4.15. Base genes in the PrOTYPE and SPOT sets are annotated with green circles, and the added genes are annotated with yellow circles. The added genes are: EGFL6, IGJ, IGKC, TP53, DKK4, MUC5B, SLC3A1, MAP1LC3A, IGFBP1, CPNE8, SERPINA5, SCGB1D2, STC1, EPAS1, BRCA1, KGFLP2, SENP8, BCL2, PBX1, KLK7, C10orf116 and LIN28B. Unused genes are annotated with red crosses.
| Set | Genes | PrOTYPE | SPOT | Optimal Set | Candidate Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base | COL11A1 | ✔ | ◉ | ||
| CD74 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| CD2 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| TIMP3 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| LUM | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| CYTIP | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| COL3A1 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| THBS2 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| TCF7L1 | ✔ | ✔ | ◉ | ||
| HMGA2 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| FN1 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| POSTN | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| COL1A2 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| COL5A2 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| PDZK1IP1 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| FBN1 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| HIF1A | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| CXCL10 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| DUSP4 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| SOX17 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| MITF | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| CDKN3 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| BRCA2 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| CEACAM5 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| ANXA4 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| SERPINE1 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| CRABP2 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| DNAJC9 | ✔ | ◉ | |||
| Candidates | EGFL6 | ◉ | 1 | ||
| IGJ | ◉ | 2 | |||
| IGKC | ◉ | 3 | |||
| TP53 | ◉ | 4 | |||
| DKK4 | ◉ | 5 | |||
| MUC5B | ◉ | 6 | |||
| SLC3A1 | ◉ | 7 | |||
| MAP1LC3A | ◉ | 8 | |||
| IGFBP1 | ◉ | 9 | |||
| CPNE8 | ◉ | 10 | |||
| SERPINA5 | ◉ | 11 | |||
| SCGB1D2 | ◉ | 12 | |||
| STC1 | ◉ | 13 | |||
| EPAS1 | ◉ | 14 | |||
| BRCA1 | ◉ | 15 | |||
| KGFLP2 | ◉ | 16 | |||
| SENP8 | ◉ | 17 | |||
| BCL2 | ◉ | 18 | |||
| PBX1 | ◉ | 19 | |||
| KLK7 | ◉ | 20 | |||
| C10orf116 | ◉ | 21 | |||
| LIN28B | ◉ | 22 | |||
| LGALS4 | ⓧ | 23 | |||
| ADCYAP1R1 | ⓧ | 24 | |||
| IL6 | ⓧ | 25 | |||
| ZBED1 | ⓧ | 26 | |||
| WT1 | ⓧ | 27 | |||
| TFF1 | ⓧ | 28 | |||
| GCNT3 | ⓧ | 29 | |||
| HNF1B | ⓧ | 30 | |||
| TFF3 | ⓧ | 31 | |||
| CYP4B1 | ⓧ | 32 | |||
| CYP2C18 | ⓧ | 33 | |||
| TSPAN8 | ⓧ | 34 | |||
| FUT3 | ⓧ | 35 | |||
| MET | ⓧ | 36 | |||
| ATP5G3 | ⓧ | 37 | |||
| SEMA6A | ⓧ | 38 | |||
| GPR64 | ⓧ | 39 | |||
| PAX8 | ⓧ | 40 | |||
| C1orf173 | ⓧ | 41 | |||
| GAD1 | ⓧ | 42 | |||
| CAPN2 | ⓧ | 43 | |||
| TPX2 | ⓧ | 44 |
4.4.2 Gene List Comparisons in Confirmation Set
We train the SMOTE-SVM workflow using four different gene lists in the confirmation set. Overall and per-class results are shown in Table 4.16. The four gene lists are:
All Overlap (n=72): all genes that are in overlap among the three CodeSets
Base (n=28): among the overlapping genes, the base set from the PrOTYPE and SPOT lists
Optimal (n=50): among the overlapping genes, the base set plus the additional number of genes that result in the optimal value for a selected evaluation metric, as assessed in Figure 4.18
Full Panel (n=151): union of all genes found in PrOTYPE and SPOT lists
| Method | Metric | Overall | HGSOC | CCOC | ENOC | MUOC | LGSOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Overlap | Accuracy | 0.822 (0.811, 0.836) | 0.85 (0.827, 0.868) | 0.969 (0.961, 0.984) | 0.869 (0.843, 0.906) | 0.978 (0.969, 0.984) | 0.978 (0.969, 0.992) |
| Sensitivity | 0.602 (0.526, 0.685) | 0.939 (0.918, 0.952) | 0.807 (0.692, 0.923) | 0.496 (0.364, 0.682) | 0.666 (0.4, 0.8) | 0.1 (0, 0.5) | |
| Specificity | 0.92 (0.904, 0.928) | 0.678 (0.585, 0.727) | 0.99 (0.974, 1) | 0.944 (0.937, 0.953) | 0.992 (0.976, 1) | 0.995 (0.984, 1) | |
| F1-Score | 0.711 (0.621, 0.78) | 0.892 (0.88, 0.904) | 0.852 (0.783, 0.923) | 0.553 (0.444, 0.714) | 0.706 (0.571, 0.833) | 0.25 (0, 0.5) | |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.761 (0.715, 0.804) | 0.808 (0.764, 0.834) | 0.898 (0.842, 0.957) | 0.72 (0.653, 0.817) | 0.829 (0.7, 0.896) | 0.548 (0.492, 0.746) | |
| Kappa | 0.632 (0.577, 0.667) | 0.648 (0.571, 0.695) | 0.835 (0.762, 0.914) | 0.478 (0.358, 0.658) | 0.696 (0.562, 0.825) | 0.095 (-0.016, 0.492) | |
| Optimal | Accuracy | 0.804 (0.787, 0.828) | 0.836 (0.803, 0.867) | 0.967 (0.945, 0.984) | 0.849 (0.814, 0.906) | 0.974 (0.969, 0.984) | 0.981 (0.969, 0.992) |
| Sensitivity | 0.597 (0.505, 0.639) | 0.913 (0.894, 0.94) | 0.835 (0.692, 0.929) | 0.485 (0.273, 0.727) | 0.554 (0.4, 0.8) | 0.2 (0, 0.5) | |
| Specificity | 0.916 (0.892, 0.928) | 0.686 (0.537, 0.75) | 0.984 (0.974, 1) | 0.922 (0.896, 0.943) | 0.992 (0.984, 1) | 0.997 (0.984, 1) | |
| F1-Score | 0.703 (0.646, 0.779) | 0.881 (0.865, 0.902) | 0.849 (0.72, 0.929) | 0.508 (0.353, 0.727) | 0.628 (0.5, 0.8) | 0.533 (0.4, 0.667) | |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.757 (0.699, 0.78) | 0.799 (0.733, 0.837) | 0.91 (0.833, 0.953) | 0.703 (0.608, 0.835) | 0.773 (0.7, 0.896) | 0.598 (0.5, 0.75) | |
| Kappa | 0.6 (0.521, 0.659) | 0.62 (0.509, 0.698) | 0.83 (0.69, 0.92) | 0.42 (0.263, 0.671) | 0.615 (0.484, 0.792) | 0.21 (0, 0.663) | |
| Base | Accuracy | 0.798 (0.752, 0.844) | 0.835 (0.783, 0.891) | 0.974 (0.946, 0.992) | 0.838 (0.783, 0.891) | 0.977 (0.969, 0.992) | 0.972 (0.953, 0.984) |
| Sensitivity | 0.676 (0.61, 0.796) | 0.868 (0.788, 0.918) | 0.865 (0.765, 1) | 0.564 (0.364, 0.864) | 0.684 (0.5, 0.8) | 0.4 (0, 1) | |
| Specificity | 0.925 (0.912, 0.945) | 0.769 (0.659, 0.844) | 0.988 (0.973, 1) | 0.892 (0.83, 0.933) | 0.99 (0.976, 1) | 0.986 (0.976, 1) | |
| F1-Score | 0.681 (0.615, 0.77) | 0.874 (0.827, 0.916) | 0.881 (0.788, 0.966) | 0.526 (0.4, 0.731) | 0.71 (0.6, 0.889) | 0.325 (0, 0.5) | |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.8 (0.776, 0.854) | 0.818 (0.777, 0.88) | 0.926 (0.869, 0.996) | 0.728 (0.648, 0.88) | 0.837 (0.746, 0.9) | 0.693 (0.488, 0.992) | |
| Kappa | 0.614 (0.549, 0.705) | 0.634 (0.537, 0.76) | 0.866 (0.757, 0.961) | 0.429 (0.306, 0.664) | 0.698 (0.584, 0.885) | 0.249 (-0.024, 0.494) | |
| Full Panel | Accuracy | 0.826 (0.798, 0.853) | 0.85 (0.822, 0.884) | 0.97 (0.953, 0.984) | 0.872 (0.837, 0.93) | 0.977 (0.969, 0.984) | 0.981 (0.969, 0.992) |
| Sensitivity | 0.605 (0.53, 0.677) | 0.932 (0.871, 0.965) | 0.835 (0.692, 0.929) | 0.525 (0.333, 0.773) | 0.583 (0.4, 0.8) | 0.15 (0, 0.5) | |
| Specificity | 0.922 (0.908, 0.935) | 0.692 (0.634, 0.75) | 0.988 (0.974, 1) | 0.94 (0.897, 0.964) | 0.994 (0.984, 1) | 0.997 (0.992, 1) | |
| F1-Score | 0.667 (0.594, 0.726) | 0.892 (0.865, 0.915) | 0.862 (0.783, 0.929) | 0.569 (0.429, 0.791) | 0.661 (0.5, 0.833) | 0.267 (0, 0.667) | |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.763 (0.719, 0.806) | 0.812 (0.776, 0.851) | 0.911 (0.842, 0.96) | 0.733 (0.649, 0.867) | 0.788 (0.7, 0.896) | 0.573 (0.496, 0.75) | |
| Kappa | 0.642 (0.576, 0.701) | 0.651 (0.582, 0.731) | 0.845 (0.762, 0.92) | 0.496 (0.365, 0.748) | 0.649 (0.484, 0.825) | 0.207 (-0.012, 0.663) |
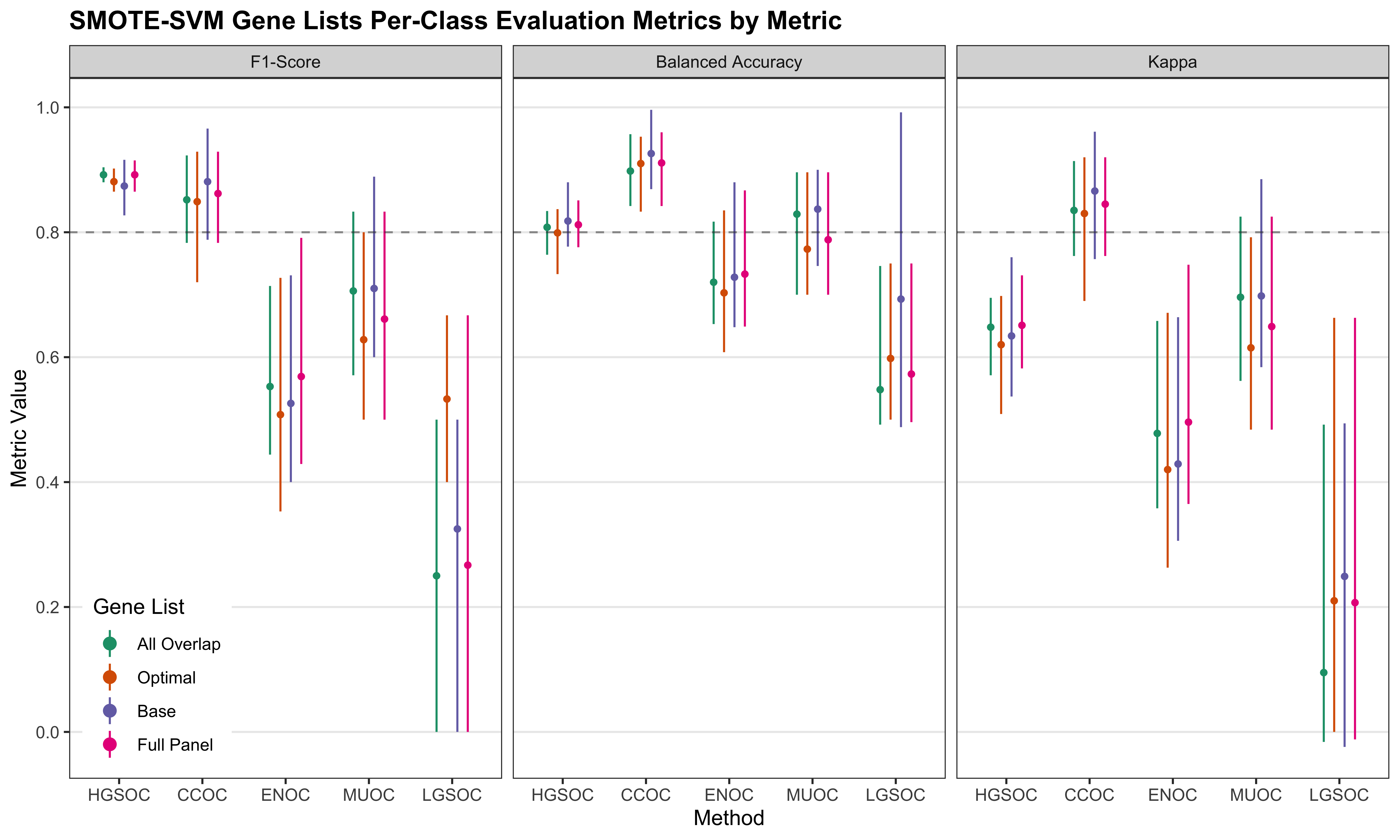
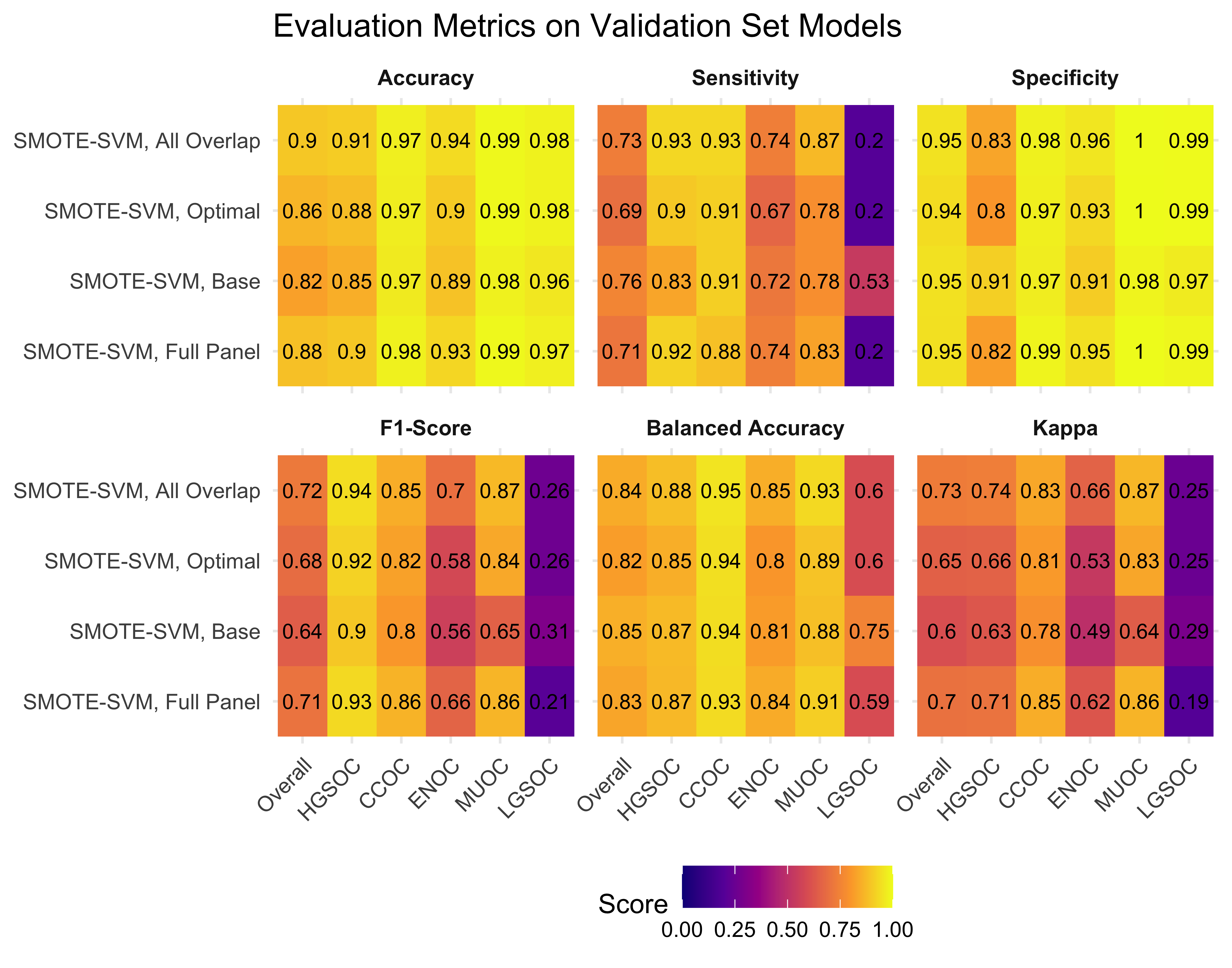
4.5 Validation Set
We assess the same four models from Table 4.16 by training on the confirmation set, and evaluating the predictions on the validation set.
4.5.1 Evaluation Metrics
| Method | Metric | Overall | HGSOC | CCOC | ENOC | MUOC | LGSOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMOTE-SVM, All Overlap | Accuracy | 0.896 | 0.907 | 0.974 | 0.936 | 0.993 | 0.981 |
| Sensitivity | 0.733 | 0.928 | 0.928 | 0.739 | 0.870 | 0.200 | |
| Specificity | 0.952 | 0.831 | 0.978 | 0.958 | 0.997 | 0.994 | |
| F1-Score | 0.723 | 0.940 | 0.848 | 0.695 | 0.870 | 0.261 | |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.842 | 0.880 | 0.953 | 0.848 | 0.933 | 0.597 | |
| Kappa | 0.730 | 0.736 | 0.834 | 0.660 | 0.866 | 0.252 | |
| SMOTE-SVM, Optimal | Accuracy | 0.862 | 0.877 | 0.970 | 0.905 | 0.992 | 0.981 |
| Sensitivity | 0.693 | 0.898 | 0.913 | 0.670 | 0.783 | 0.200 | |
| Specificity | 0.939 | 0.800 | 0.975 | 0.931 | 0.998 | 0.994 | |
| F1-Score | 0.684 | 0.919 | 0.824 | 0.581 | 0.837 | 0.261 | |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.816 | 0.849 | 0.944 | 0.800 | 0.890 | 0.597 | |
| Kappa | 0.653 | 0.659 | 0.807 | 0.529 | 0.833 | 0.252 | |
| SMOTE-SVM, Base | Accuracy | 0.820 | 0.849 | 0.965 | 0.887 | 0.979 | 0.960 |
| Sensitivity | 0.755 | 0.831 | 0.913 | 0.716 | 0.783 | 0.533 | |
| Specificity | 0.948 | 0.913 | 0.970 | 0.906 | 0.984 | 0.967 | |
| F1-Score | 0.643 | 0.896 | 0.803 | 0.555 | 0.655 | 0.308 | |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.852 | 0.872 | 0.941 | 0.811 | 0.883 | 0.750 | |
| Kappa | 0.602 | 0.627 | 0.784 | 0.494 | 0.644 | 0.291 | |
| SMOTE-SVM, Full Panel | Accuracy | 0.884 | 0.896 | 0.978 | 0.926 | 0.993 | 0.974 |
| Sensitivity | 0.713 | 0.918 | 0.884 | 0.739 | 0.826 | 0.200 | |
| Specificity | 0.947 | 0.815 | 0.985 | 0.947 | 0.998 | 0.987 | |
| F1-Score | 0.705 | 0.932 | 0.859 | 0.663 | 0.864 | 0.207 | |
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.830 | 0.867 | 0.935 | 0.843 | 0.912 | 0.594 | |
| Kappa | 0.700 | 0.706 | 0.847 | 0.622 | 0.860 | 0.194 |
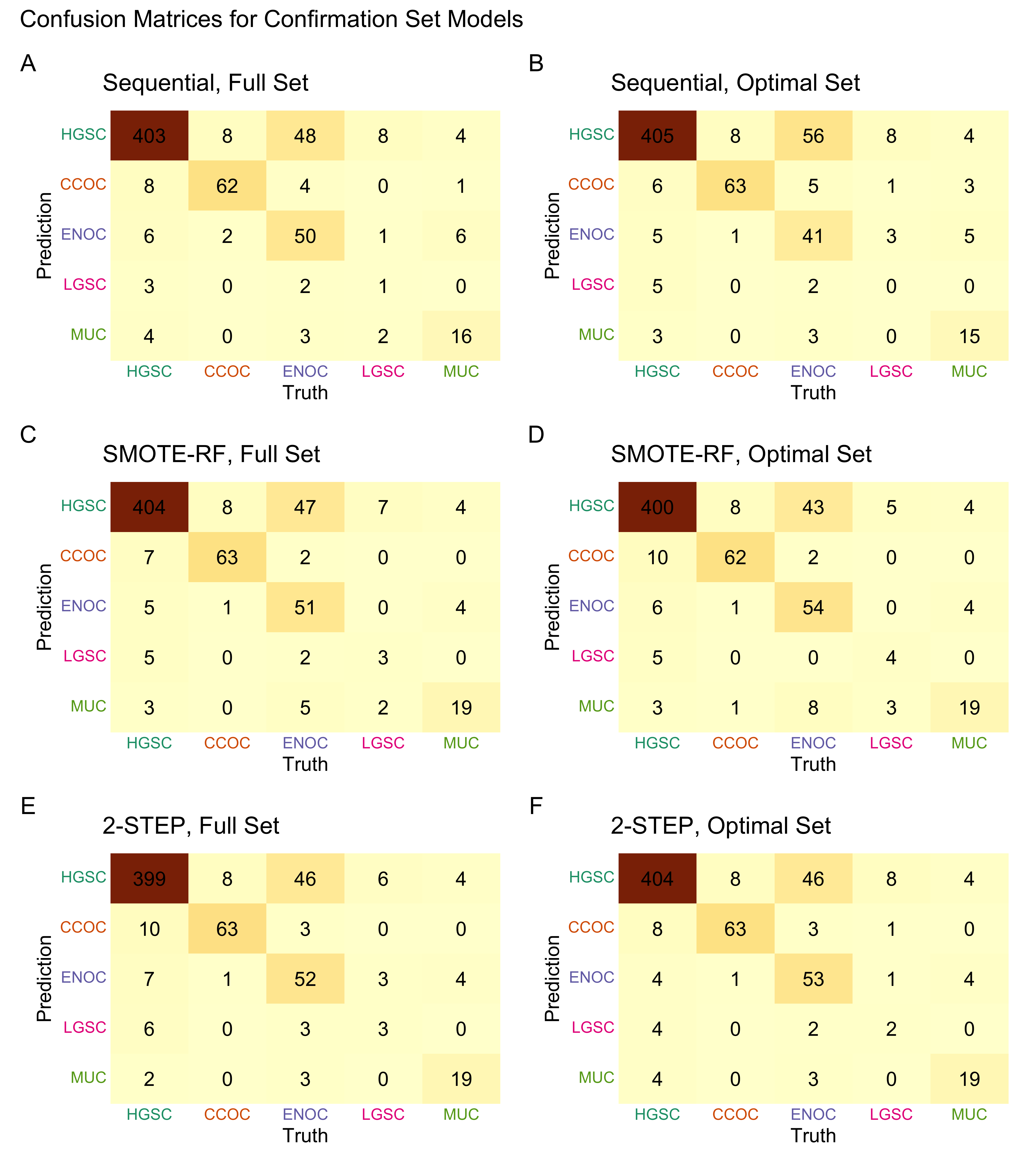
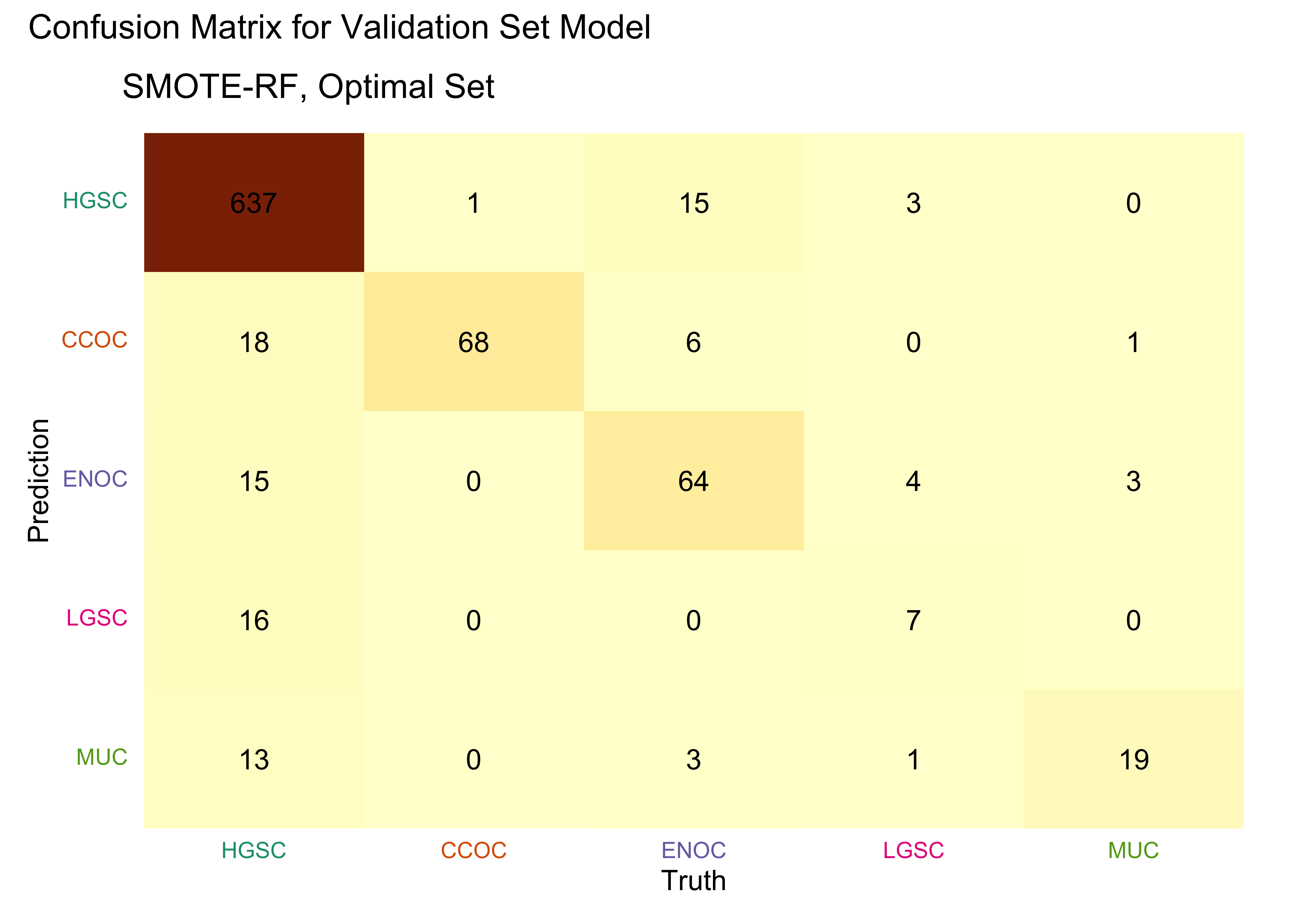
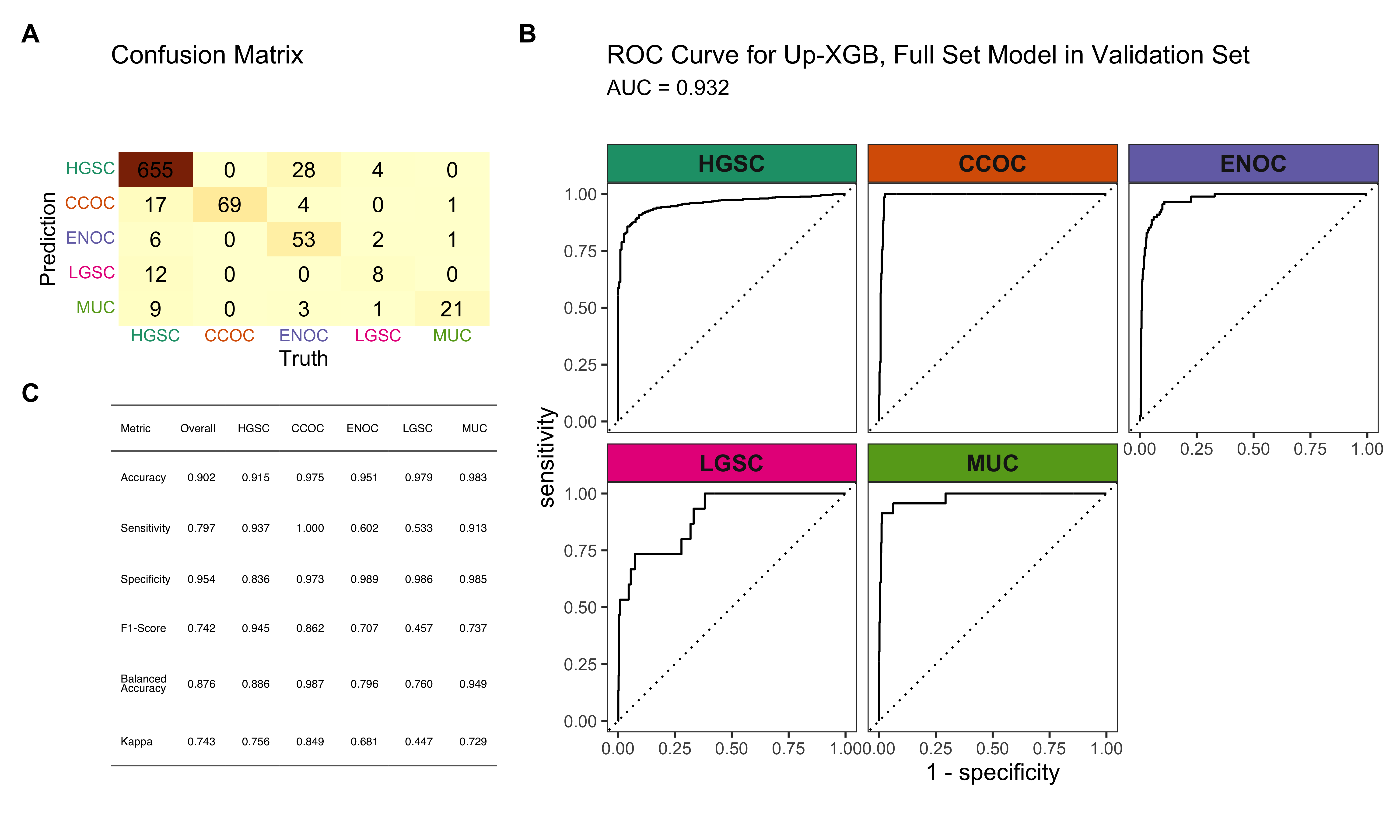
4.5.2 Confusion Matrices
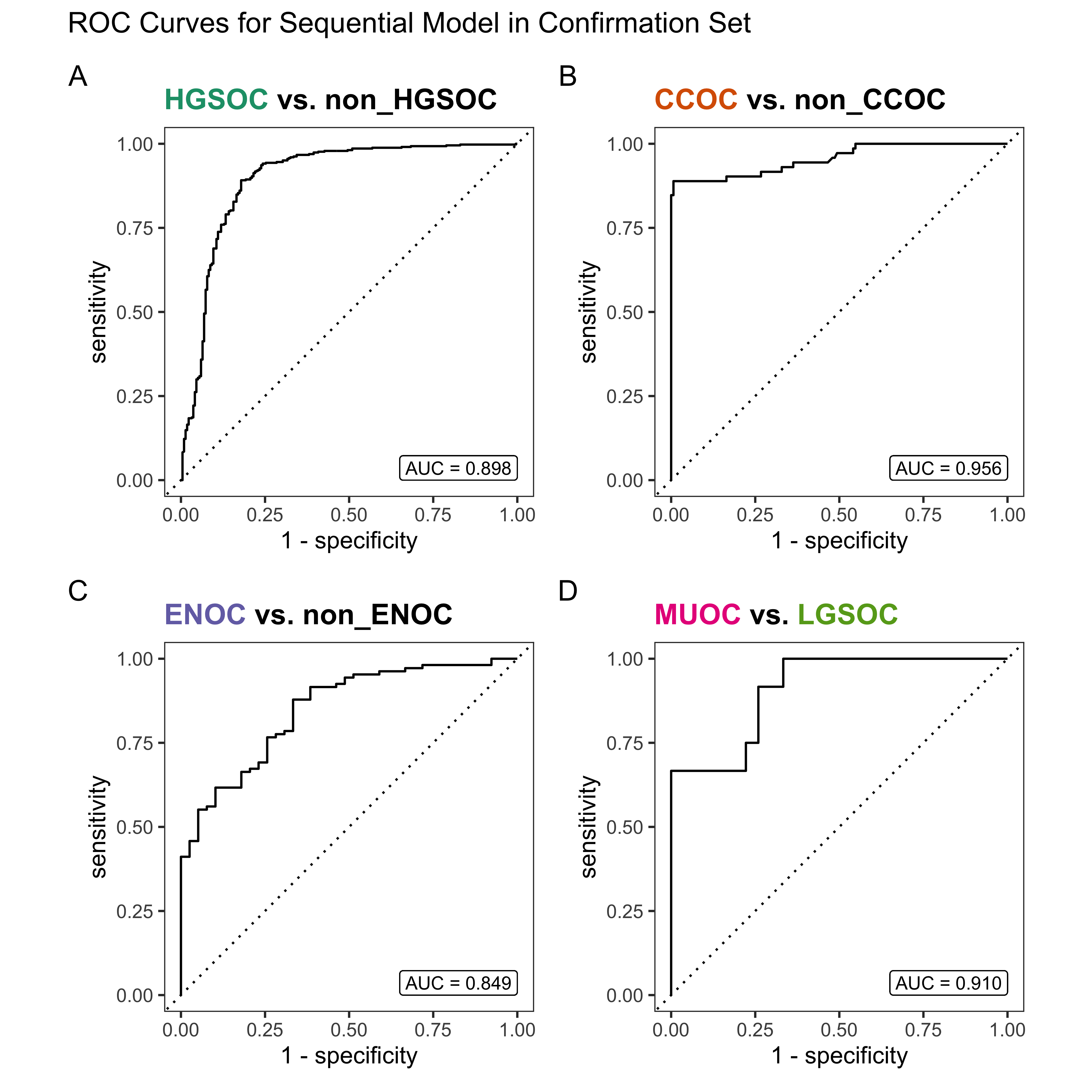
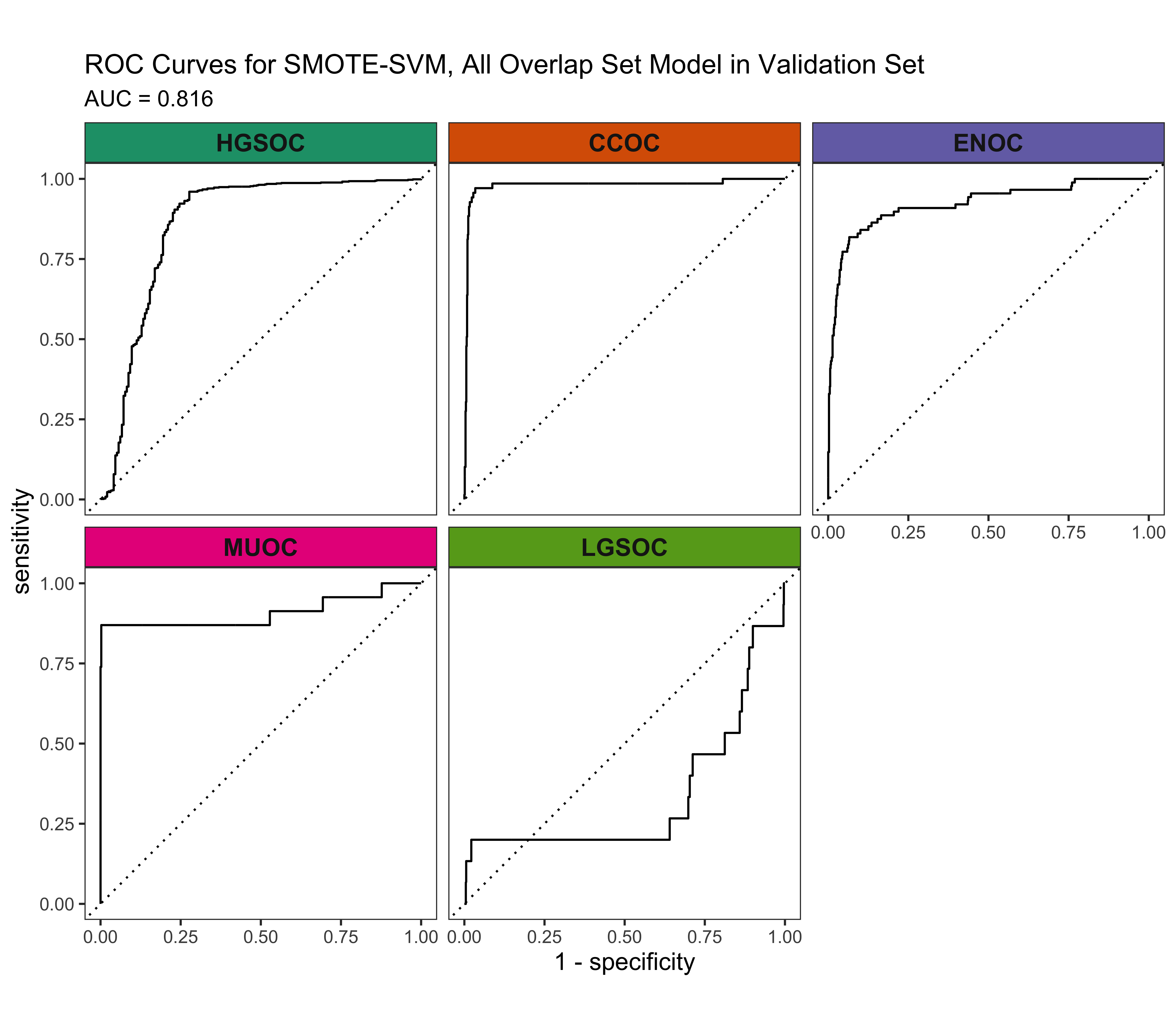
4.5.3 ROC Curves
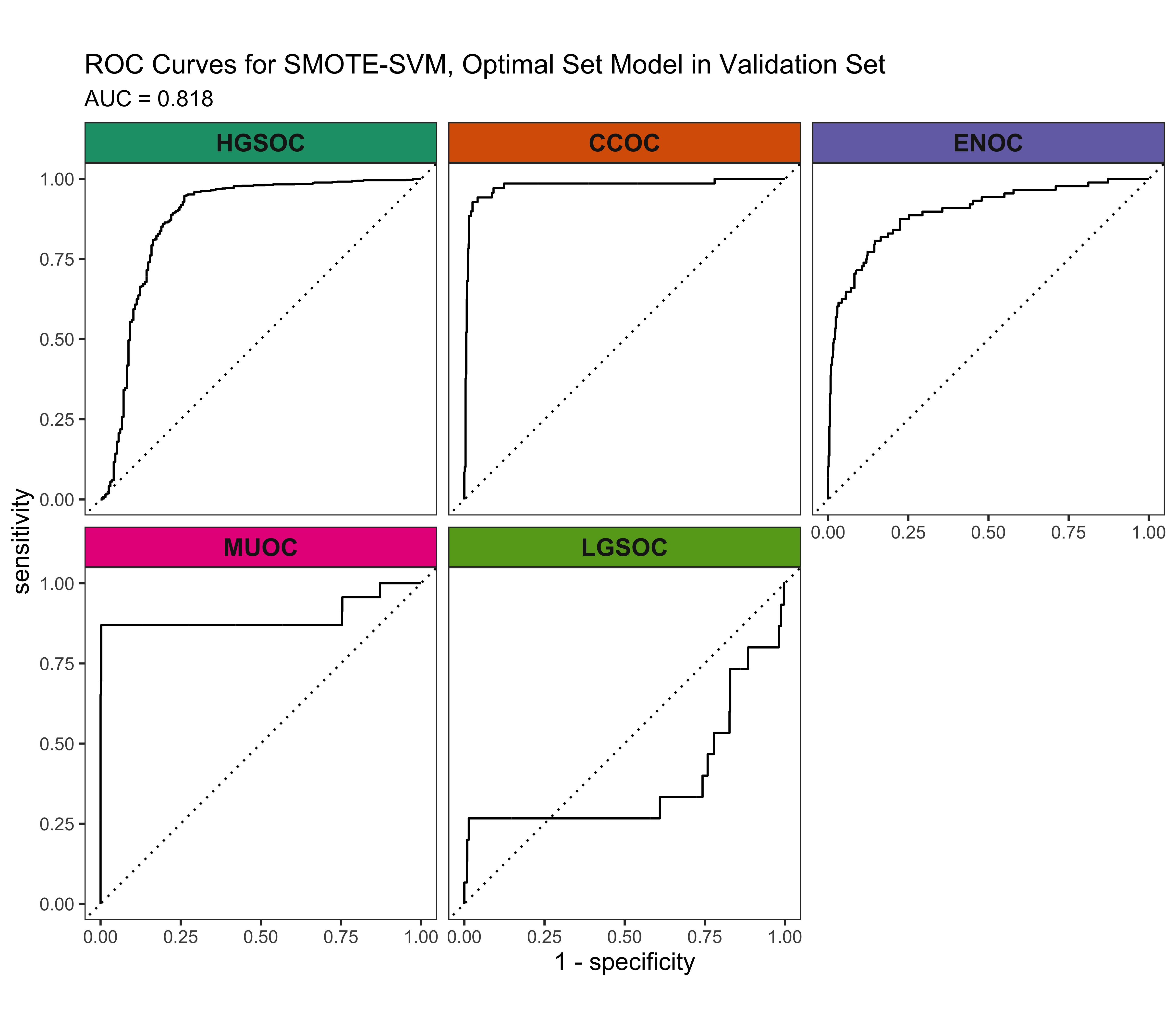
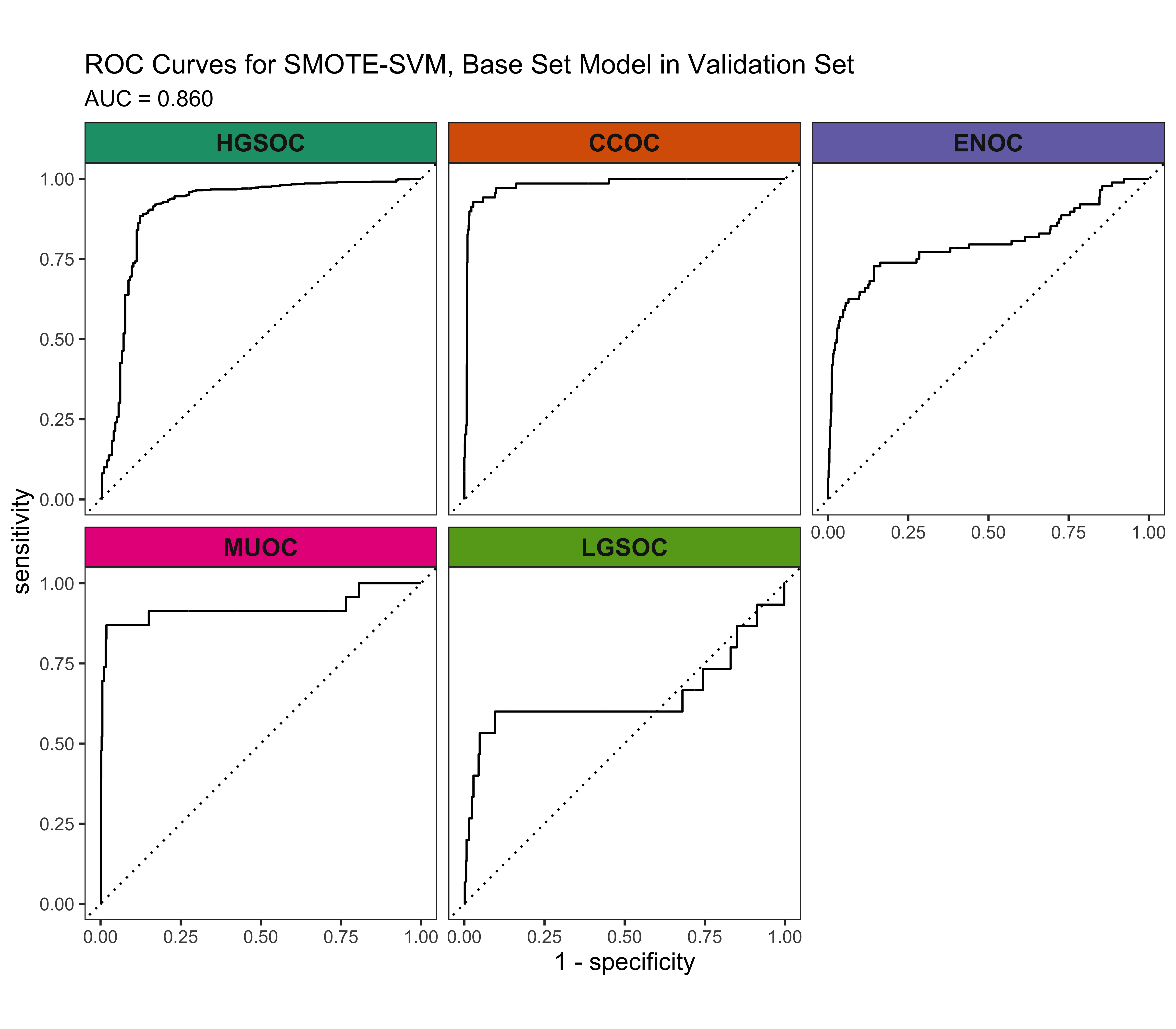
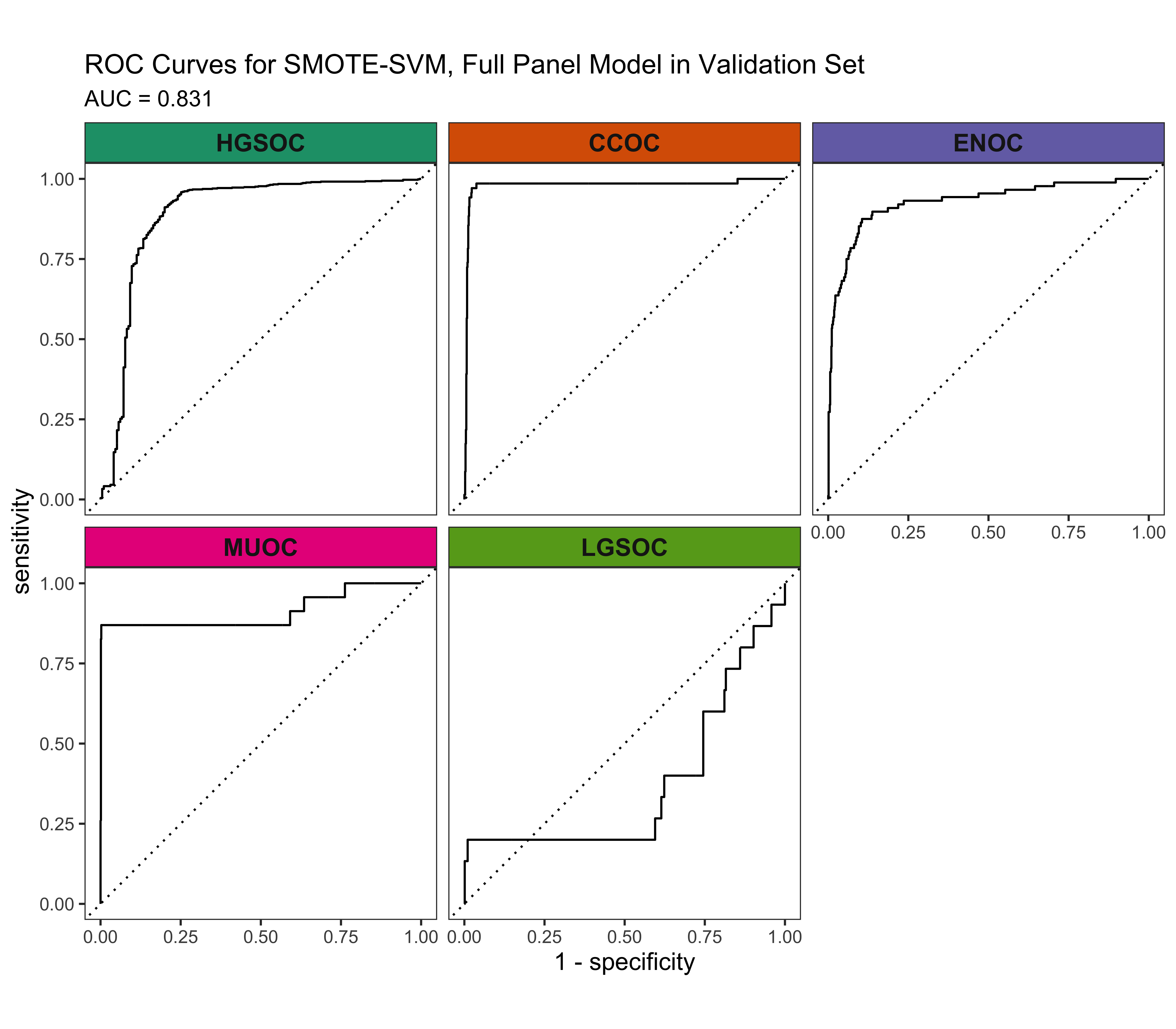
4.5.4 Calibration Plots
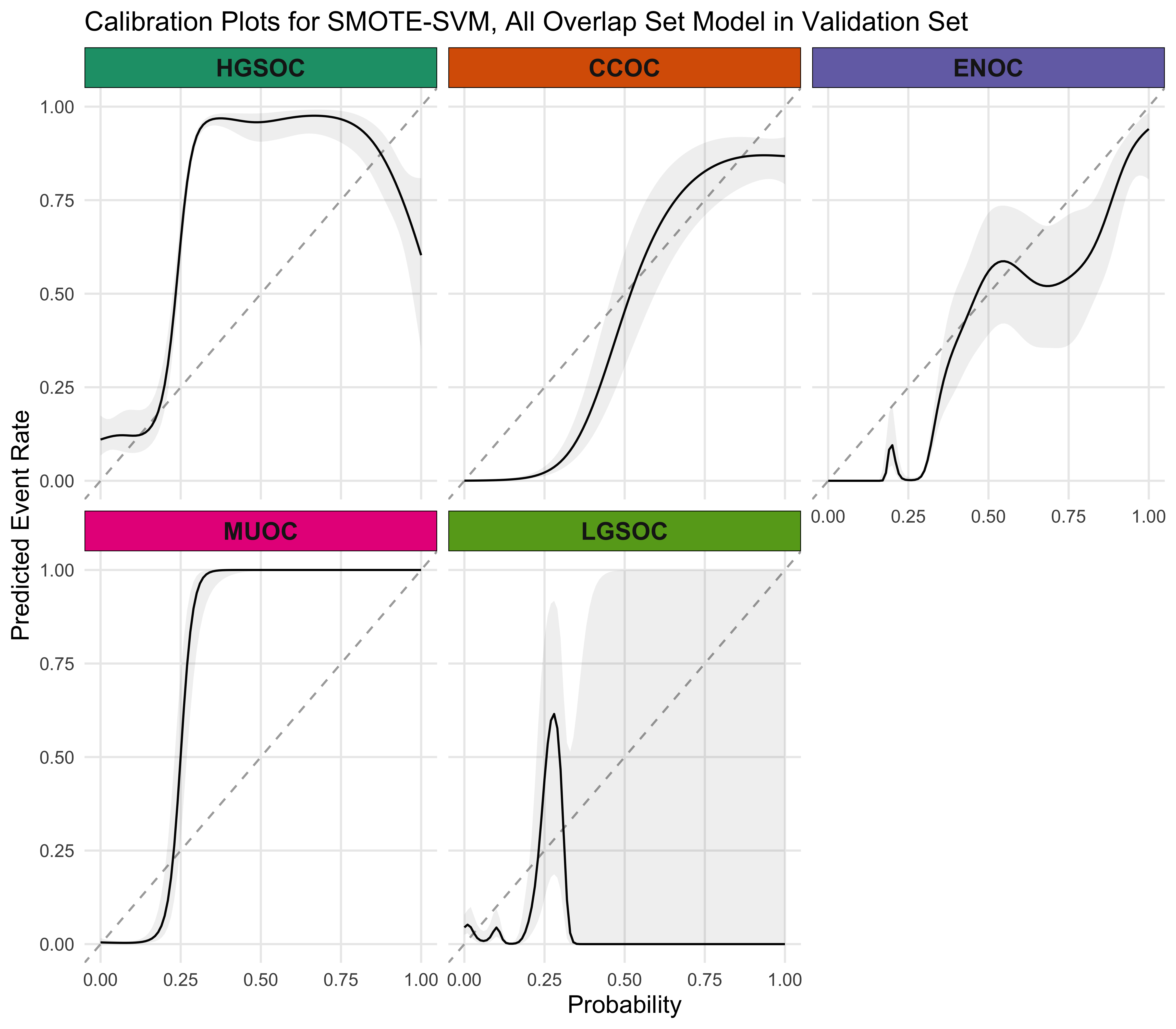
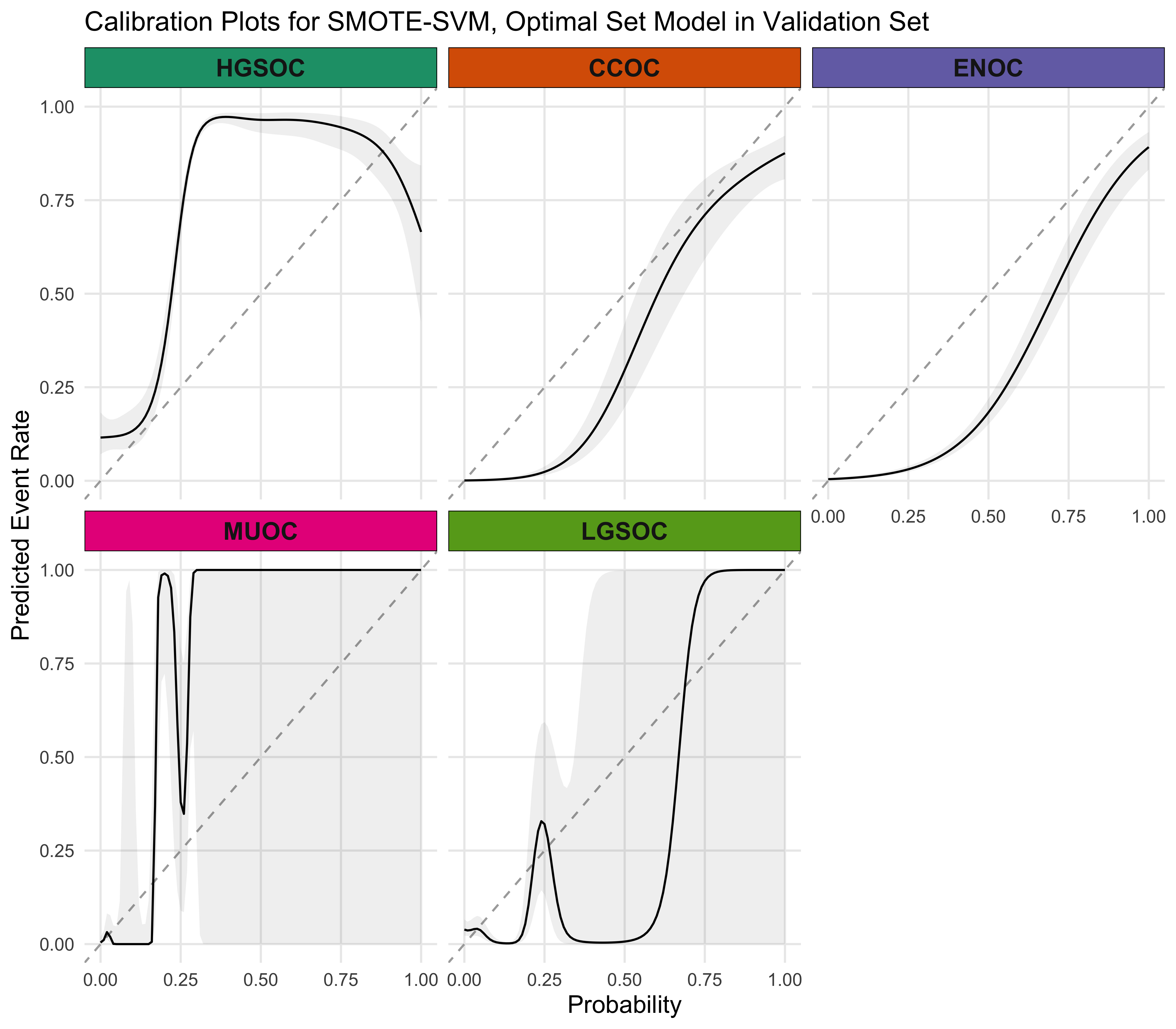
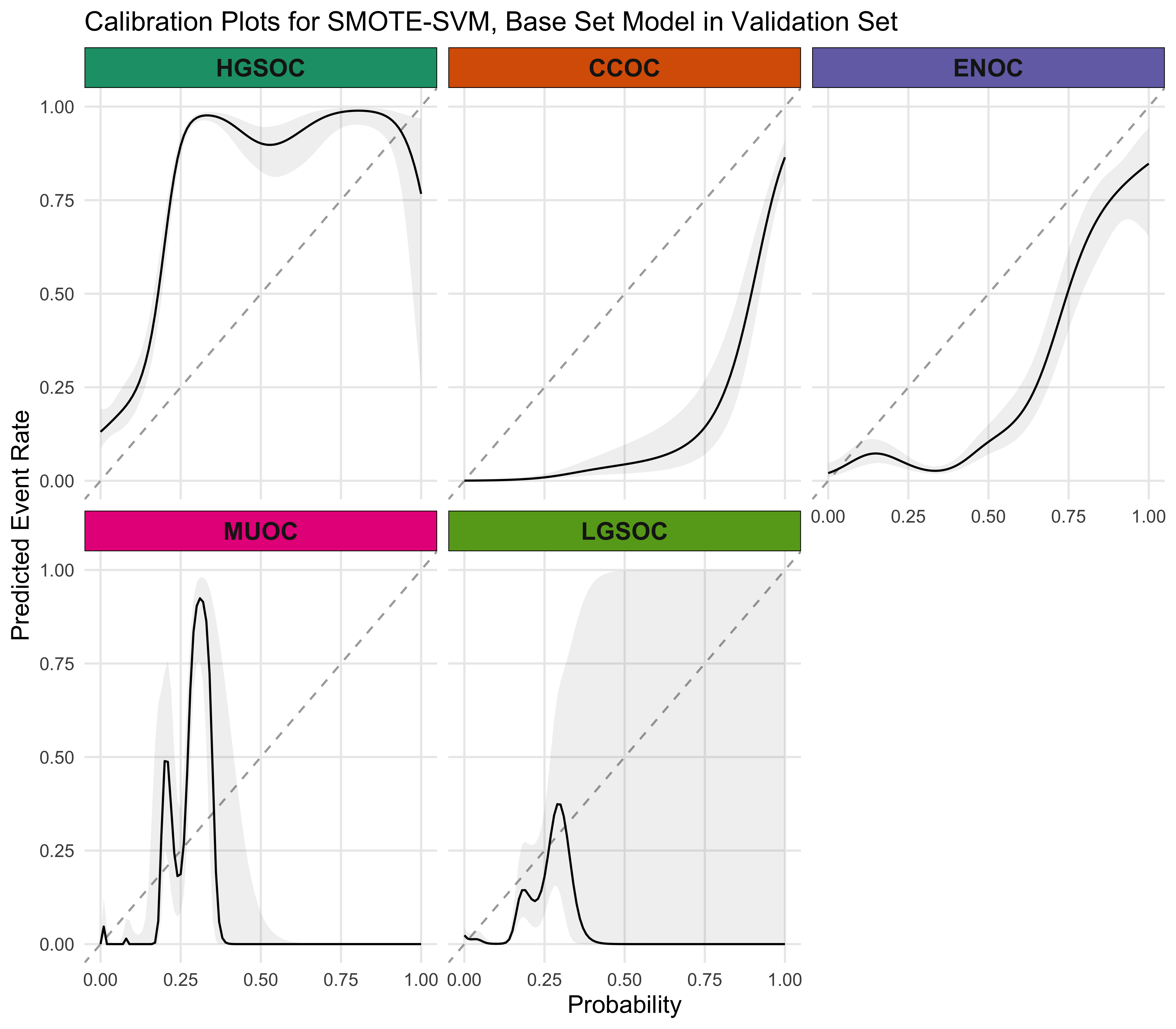
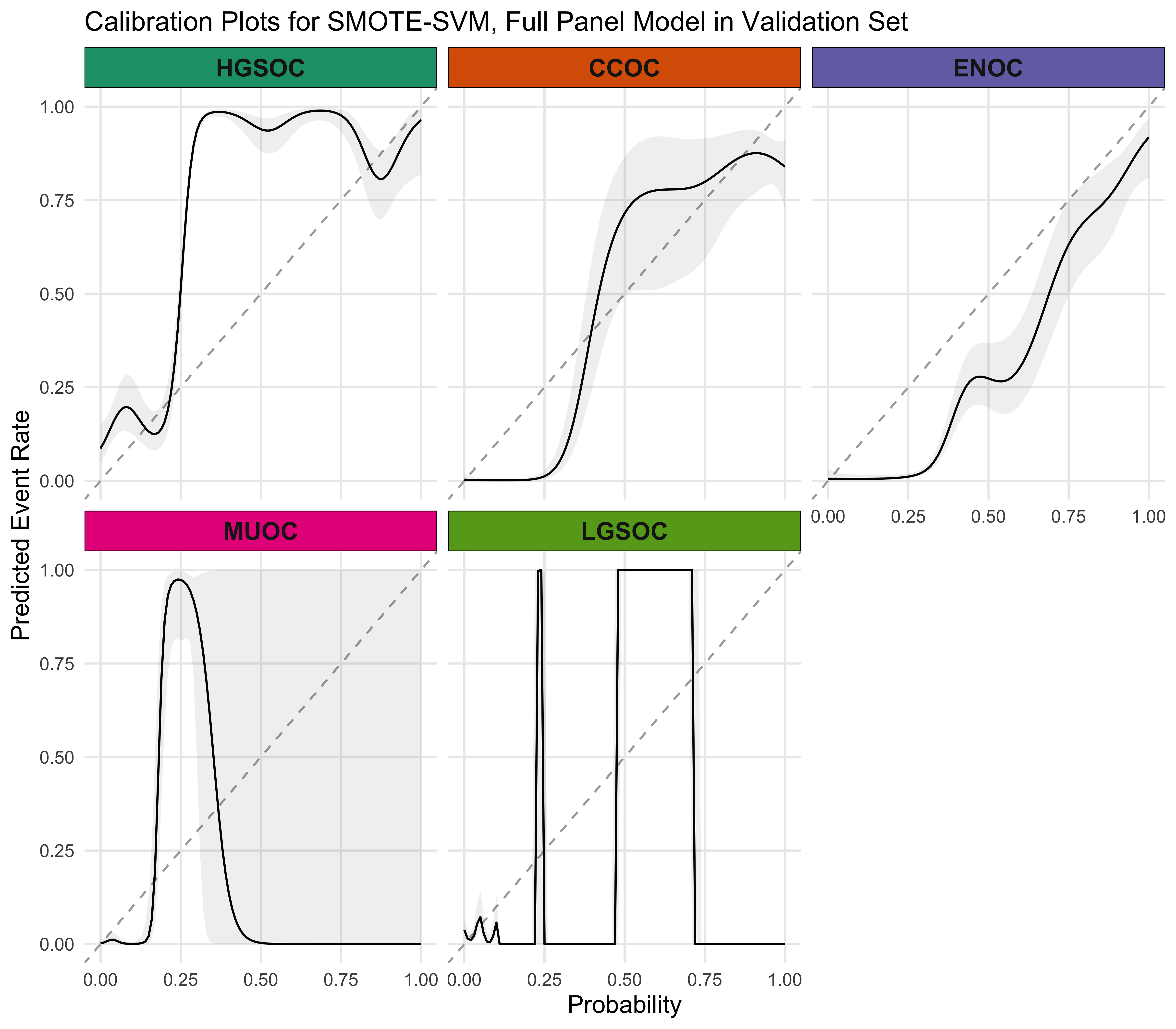
4.5.5 Summary
The SMOTE-SVM, All Overlap model has the highest overall F1-Score. A summary of pertinent results are shown in Figure 4.30.
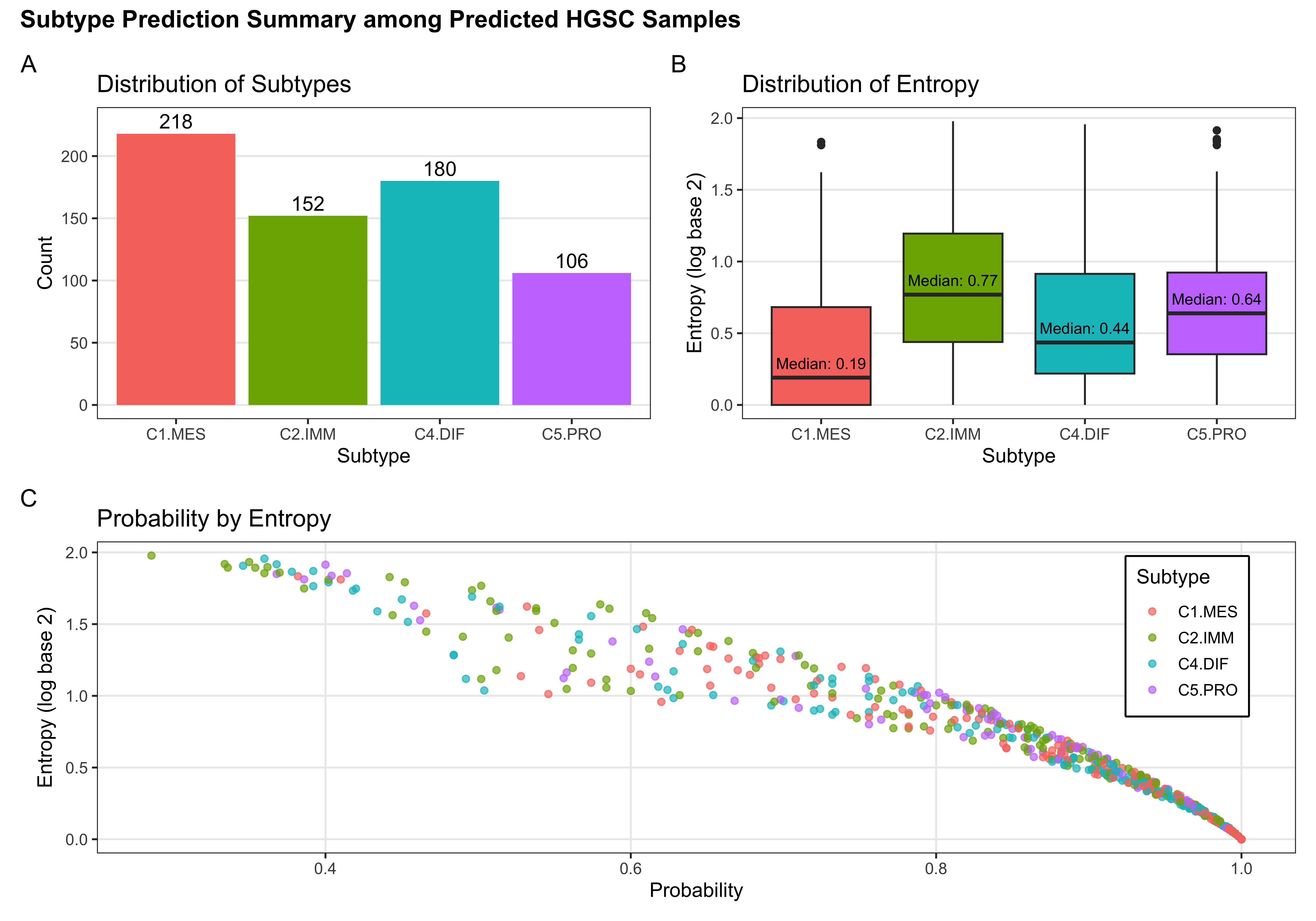
4.5.6 Additional Explorations
| Characteristic | Predicted ENOC Correctly N = 651 |
Missed ENOC N = 231 |
p-value2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis | 53 (46, 62) | 59 (51, 65) | 0.064 |
| Tumour grade | 0.037 | ||
| low grade | 46 (88%) | 13 (65%) | |
| high grade | 6 (12%) | 7 (35%) | |
| Unknown | 13 | 3 | |
| FIGO tumour stage | 0.2 | ||
| I | 48 (75%) | 14 (61%) | |
| II-IV | 16 (25%) | 9 (39%) | |
| Unknown | 1 | 0 | |
| Race | 0.4 | ||
| white | 57 (93%) | 19 (86%) | |
| non-white | 4 (6.6%) | 3 (14%) | |
| Unknown | 4 | 1 | |
| ARID1A | >0.9 | ||
| absent/subclonal | 12 (18%) | 4 (17%) | |
| present | 53 (82%) | 19 (83%) | |
| WT1 | 0.5 | ||
| diffuse (>50%) | 3 (4.6%) | 2 (8.7%) | |
| focal (1-50%) | 3 (4.6%) | 0 (0%) | |
| negative | 59 (91%) | 21 (91%) | |
| TP53 | 0.6 | ||
| mutated | 3 (4.6%) | 2 (9.1%) | |
| wild type | 62 (95%) | 20 (91%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| PR | 0.026 | ||
| diffuse (>50%) | 39 (60%) | 7 (30%) | |
| focal (1-50%) | 11 (17%) | 4 (17%) | |
| negative | 15 (23%) | 12 (52%) | |
| P16 | 0.3 | ||
| abnormal block | 3 (4.6%) | 3 (13%) | |
| abnormal complete absence | 18 (28%) | 7 (30%) | |
| normal | 44 (68%) | 13 (57%) | |
| NAPSIN A | >0.9 | ||
| negative | 63 (97%) | 22 (100%) | |
| positive | 2 (3.1%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| 1 Median (Q1, Q3); n (%) | |||
| 2 Wilcoxon rank sum test; Fisher’s exact test; Pearson’s Chi-squared test | |||